API Gateways with Dedicated Backends¶
We can extend the multiple gateway environments feature by utilizing parameterized endpoint capabilities of WSO2 API Manager to have each gateway point to a different back-end endpoint. API Gateway is the actual runtime of the APIs that are developed and published from the API Publisher. WSO2 API Manager is capable of publishing APIs to different Gateways where API users connect to those API Gateways in order to do the actual API calls through the applications to which they are subscribed.
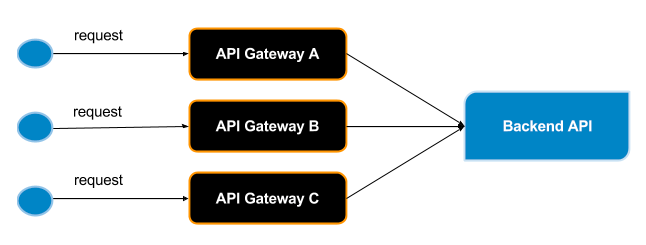
However, the API Publisher can only provide a single static endpoint for an API in the implementation. Therefore, the API call is directed to a single endpoint in whichever Gateway the API is deployed in, as depicted in the diagram below.
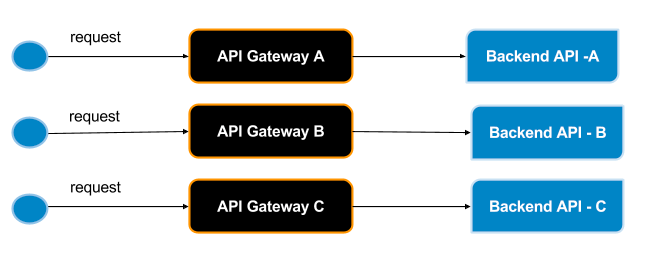
However, in most situations, you would want to have each Gateway proxying to a dedicated backend API. To provide that capability, WSO2 API Manager provides the ability to specify parameterized endpoint URLs at the time of specifying the API endpoint URL. This URL is resolved at runtime with the details (host and port) specified at the startup of each Gateway. Each gateway then points to a dedicated backend API, as depicted in the diagram below.
Configuring Parameterized Endpoints¶
Follow the steps below to configure a parameterized endpoint as the API endpoint.
- Start the WSO2 API Manager server that includes the API Publisher component and create an API.
-
Go to the Endpoints tab of the API and replace the host and port of the API endpoint with
{uri.var.host}and{uri.var.port}respectively, as shown below. -
Save and publish the API.
-
Navigate to the
<API-M_HOME>/repository/deployment/server/synapse-configs/sequencesdirectory of each Gateway and create the following sequence.<sequence xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" name="WSO2AM--Ext--In"> <property name="uri.var.host" expression="get-property('system','host')" /> <property name="uri.var.port" expression="get-property('system','port')" /> </sequence>Note
Java system properties are used at the server start-up process of each Gateway to resolve the variables that are defined as properties in this sequence.
Info
Alternatively, you can resolve this host and port using a class mediator. To do that, follow the steps below as an alternative to step 4.
1. Create a java class extending the AbstractMediator class of
org.synapse.coreas shown below and create the JAR file out of it.2. Add the created JAR file into theimport org.apache.synapse.MessageContext; import org.apache.synapse.mediators.AbstractMediator; public class EnvironmentResolver extends AbstractMediator { @Override public boolean mediate(MessageContext messageContext) { String host = System.getProperty("environment.host"); String port = System.getProperty("environment.port"); messageContext.setProperty("uri.var.host", host); messageContext.setProperty("uri.var.port", port); return true; } @Override public boolean isContentAware(){ return false; } }<API-M_HOME>/repository/components/libfolder of each Gateway. You can download a sample JAR file here.
3. Add the following sequence to the<API-M_HOME>/repository/deployment/server/synapse-configs/sequencesfolder of each Gateway.<sequence xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" name="WSO2AM--Ext--In"> <class name="org.wso2.carbon.env.EnvironmentResolver"/> </sequence>Note
org.wso2.carbon.env.EnvironmentResolveris the fully qualified name of the class that contains the code responsible for converting system variables into properties. It is a special class that needs to be extended from theorg.apache.synapse.mediators.AbstractMediatorclass and requires overriding of themediatefunction. -
Execute the following command when starting up each Gateway to set the system variables at the server start up from within the
<API-M_HOME>/bindirectory by replacing the following values.<ip_of_backend_environment> <port_of_backend_environment> host IP of the Gateway port where the Gateway is running in the dedicated machine or VM Note
If you have used the class mediator to configure API Gateways in step 4, use the command given below instead of the one above.
Now the Gateways have started with the dedicated backend host/port combinations.
-
Invoke the API.
You receive the response from the API, which is sent through the dedicated backend, from the Gateway that this API is published.