ELK Based Analytics Installation Guide¶
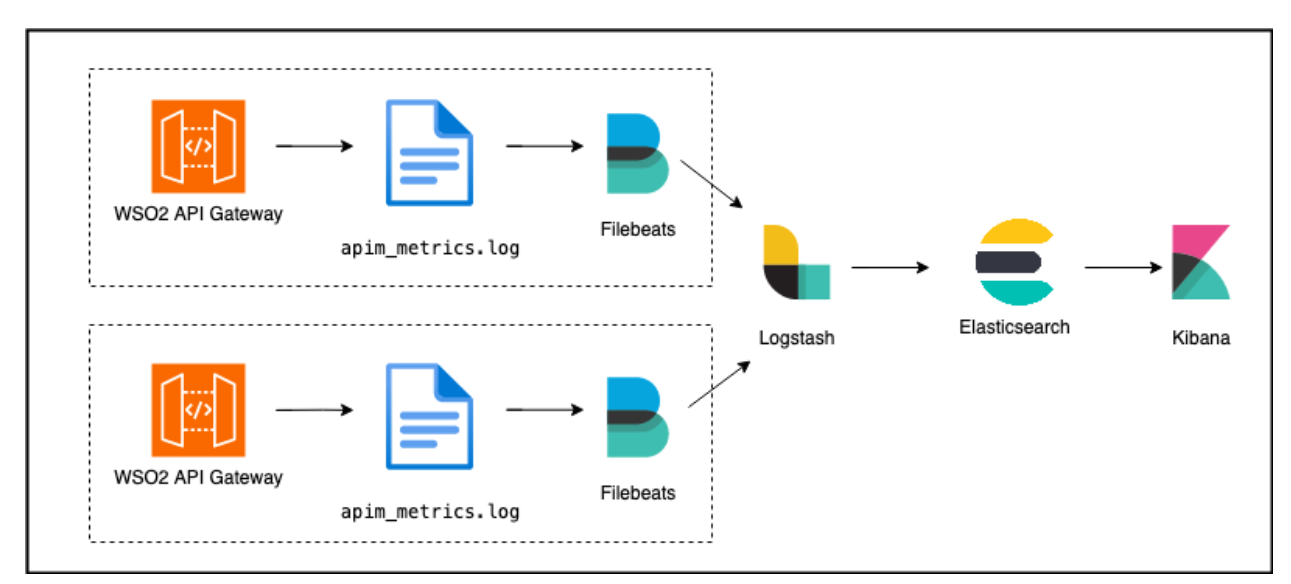
Analytics Data flow¶
The new On-Premise Analytics solution for WSO2 API Manager will publish analytics data into a log file and that file will be used as the source for the analytics solution.
ELK based WSO2 API Manager On-Premise Analytics deployment architecture has 4 main components.
- Filebeats
- Logstash
- Elasticsearch
- Kibana
This section will cover the steps required to configure the WSO2 API-M and then publish it to an external ELK cluster.
Note
The solution is developed on ELK 8.1.0 and will only be supported in Kibana versions 8.0.0 and higher.
Step 1 - Configuring API Manager¶
Step 1.1 - Configuring the deployment.toml file.¶
The Choreo based analytics will be enabled by default. Specify the type as elk to enable ELK analytics as shown below.
Open the wso2am-4.x.x/repository/conf directory. Edit apim.analytics configurations in the deployment.toml file with the following configuration.
[apim.analytics]
enable = true
type = "elk"
Step 1.2 - Enabling Logs¶
Open the wso2am-4.x.x/repository/conf directory. To enable logging for a reporter, edit the log4j2.properties file following the instructions given below.
-
Add APIM_METRICS_APPENDER to the appenders list:
appenders = APIM_METRICS_APPENDER, .... (list of other available appenders) -
Add the following configuration after the appenders:
appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.type = RollingFile appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.name = APIM_METRICS_APPENDER appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.fileName = ${sys:carbon.home}/repository/logs/apim_metrics.log appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.filePattern = ${sys:carbon.home}/repository/logs/apim_metrics-%d{MM-dd-yyyy}-%i.log appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.layout.type = PatternLayout appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.layout.pattern = %d{HH:mm:ss,SSS} [%X{ip}-%X{host}] [%t] %5p %c{1} %m%n appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.policies.type = Policies appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.policies.time.type = TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.policies.time.interval = 1 appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.policies.time.modulate = true appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.policies.size.type = SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.policies.size.size=1000MB appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.strategy.type = DefaultRolloverStrategy appender.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.strategy.max = 10 -
Add a reporter to the loggers list:
loggers = reporter, ...(list of other available loggers) -
Add the following configurations after the loggers:
logger.reporter.name = org.wso2.am.analytics.publisher.reporter.elk logger.reporter.level = INFO logger.reporter.additivity = false logger.reporter.appenderRef.APIM_METRICS_APPENDER.ref = APIM_METRICS_APPENDER
Note
The apim_metrics.log file be rolled each day or when the log size reaches the limit of 1000 MB by default. Furthermore, only 10 revisions will be kept and older revisions will be deleted automatically. You can change these configurations by updating the configurations provided in step 2 given above in this. section.
Step 2 - Configuring ELK¶
Installing Elasticsearch¶
-
Install Elasticsearch according to your operating system.
-
Make sure Elasticsearch is up and running.
Info
As recommended by ELK, a minimum 3 node cluster is required for a production environment.
Installing Filebeat¶
-
Install Filebeat according to your operating system.
-
Configure Filebeats to read the log file in the
repository/logsfolder.filebeat.inputs: - type: log enabled: true paths: - {apim_home}/repository/logs/apim_metrics.log include_lines: ['(apimMetrics):'] output.logstash: # The Logstash hosts hosts: ["{LOGSTASH_URL}:5044"]
Installing Logstash¶
- Install Logstash according to your operating system.
-
Add the following content to a file (eg: logstash-sample.conf)
3. Start the server ./logstash -f {FilePathToConfig}/logstash-sample.confinput { beats { port => 5044 } } filter { grok { match => ["message", "%{GREEDYDATA:UNWANTED}\ apimMetrics:%{GREEDYDATA:apimMetrics}\, %{GREEDYDATA:UNWANTED} \:%{GREEDYDATA:properties}"] } json { source => "properties" } } output { if [apimMetrics] == " apim:response" { elasticsearch { hosts => ["http://{ELK_URL}:9200"] index => "apim_event_response" user => "elastic" password => "Admin1234" } } else if [apimMetrics] == " apim:faulty" { elasticsearch { hosts => ["http://{ELK_URL}:9200"] index => "apim_event_faulty" user => "elastic" password => "Admin1234" } } }
Installing Kibana¶
-
Install Kibana according to your operating system.
-
Launch the Kibana web interface.
-
Log in to the Kibana dashboards.
-
Navigate to Stack Management > index pattern. If you already have any index patterns created under the following names, delete them before importing the saved artifacts.
apim_event* apim_event_faulty apim_event_response -
Download the artifact file from below.
Artifacts v1 - here
Artifacts v2 - here - Navigate to Stack Management > Saved Object and click on Import. Add the downloaded artifact file as an import object, and import
Info
Follow the recommendations of Elastic in order to optimize the performance of the system.
Step 3 - Configure Security in ELK¶
Elastic search supports several authentication modes ranging from basic authentication to Single sign-on with several identity providers.
In this section, we mainly focus on configuring single-sign-on with WSO2 API Manager via OpenID Connect. If you are looking for other supported authentication providers, refer the ElasticSearch documentation.
Info
Note that you can either configure Basic Authentication or SSO with OpenID Connect.
Configure Basic Authentication¶
ElasticSearch supports basic authentication via an internal user store. If you need to set up basic authentication in ElasticSearch and Kibana, refer the ElasticSearch documentation.
Configure Single-Sign-On with WSO2 API Manager via OpenID Connect¶
ElasticSearch/Kibana deployment can be configured to enable Single-sign-on with WSO2 API Manager via OpenID Connect. To set up SSO with WSO2 API Manager, follow the steps given below.
Prerequisite
To enable Single-sign-on security features in ELK, an ElasticSearch Platinum subscription is required.
Configure a service provider at WSO2 API Manager¶
To enable SSO with WSO2 API Manager, a service provider needs to be created. Follow the steps given below to create a service provider.
- Login to the WSO2 API Manager management console via
https://<API-M_HOST>:9443/carbon. -
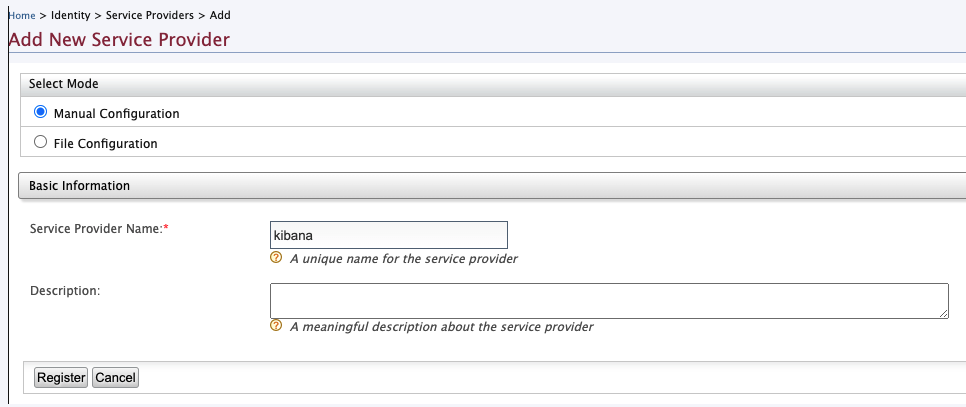
From the Main, click Add under the Service Providers section.
-
In the Add New Service Provider page, create a new service provider by providing the service provider name (e.g.,kibana).
-
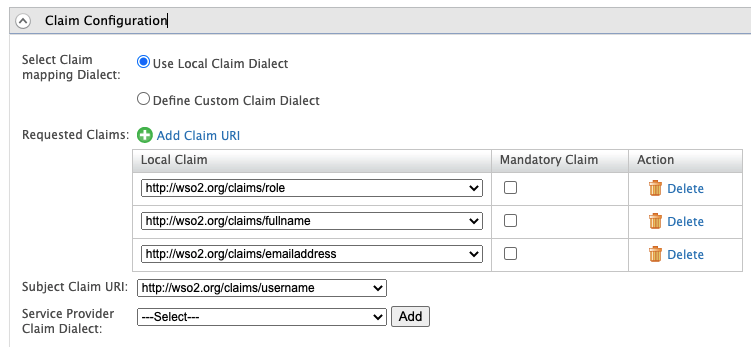
Once the service provider is created, go to the service provider, expand the Claim Configuration section. Configure the claims as shown in the image below and click Update.
-
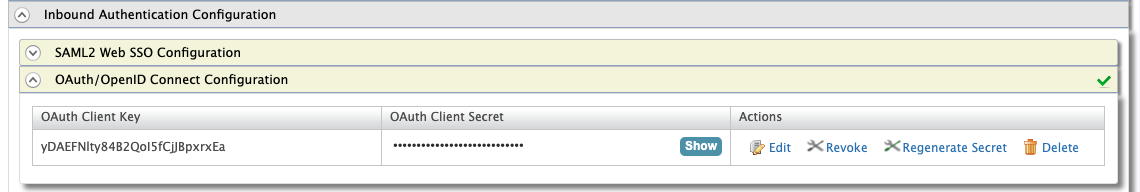
Expand the Inbound Authentication Configuration section, then OAuth/OpenID Connect Configuration and click Edit.
-
In the View/Update Application Settings page, set the
callback URLas follows.regexp=(https://kibana.example.com:5601/api/security/oidc/callback|https://kibana.example.com:5601/security/logged_out)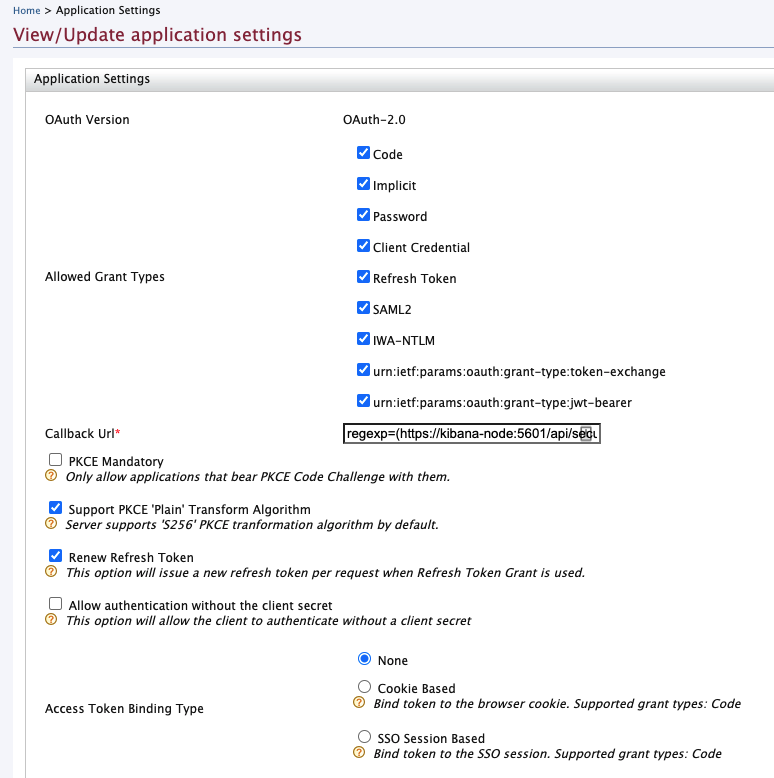
-
Click Update to save your changes.
Configure OIDC realm in Elastic Search¶
To configure single sign-on to the Elastic Stack using OpenID connect, follow the steps given here.
A sample OpenID connect realm is as follows.
OpenID Connect realm configurations¶
xpack.security.authc.realms.oidc.oidc1:
order: 2
rp.client_id: "<CLIENT_ID>"
rp.response_type: code
rp.redirect_uri: "https://kibana.example.com:5601/api/security/oidc/callback"
op.issuer: "https://apim.example.com:9443/oauth2/token"
op.authorization_endpoint: "https://apim.example.com:9443/oauth2/authorize"
op.token_endpoint: "https://apim.example.com:9443/oauth2/token"
op.jwkset_path: "https://apim.example.com:9443/oauth2/jwks"
op.endsession_endpoint: "https://apim.example.com:9443/oidc/logout"
rp.post_logout_redirect_uri: "https://kibana.example.com:5601/security/logged_out"
claims.principal: sub
claims.groups: groups
ssl.verification_mode: none
claims.name: name
claims.mail: email
Configure Role Mapping for Kibana dashboard¶
Once the above steps are completed, role mapping needs to be configured in Kibana to allow WSO2 API Manager users to access the dashboards in Kibana. For that follow the steps mentioned below.
Create Users and Roles in WSO2 API Manager¶
-
Login to WSO2 API Manager management console via
https://<API-M_HOST>:9443/carbon. -
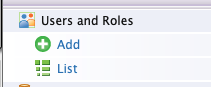
From the Main menu in the left panel, click Add under the Users and Roles section.
-
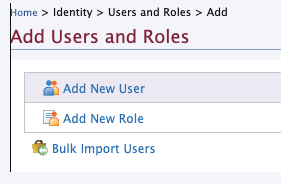
In Add Users and Roles, click Add new role.
-
Create a new role (e.g.,
AnalyticsViewer) and click Finish. -
In Add Users and Roles, click Add new user.
-
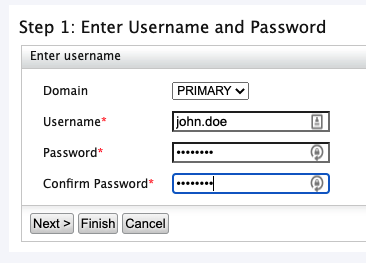
Create a new user and click the Next.
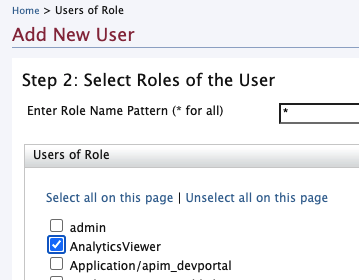
-
In the “Step 2: Select Roles of the User” page select the previously created role and click “Finish”.
Create role mapping¶
- Login to Kibana using basic authentication and go to Stack Management under the Management section in the left menu. Click Role Mappings under the Security section.
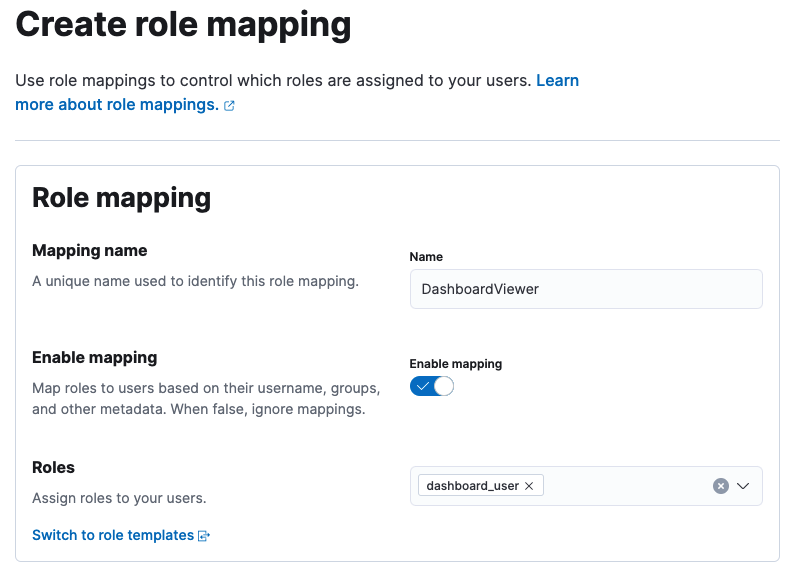
- In the Create Role Mapping section, add a new role mapping by providing a Mapping name.
-
Select a role that has access to the particular dashboard from the Roles.
-
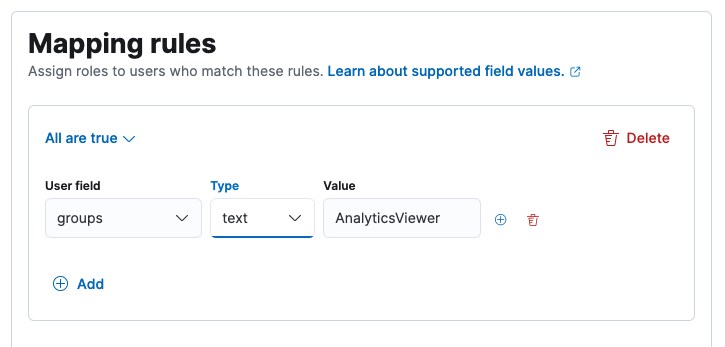
Under Mapping Rules select groups as the user field and name of the previously-created role as the value and click Add.
-
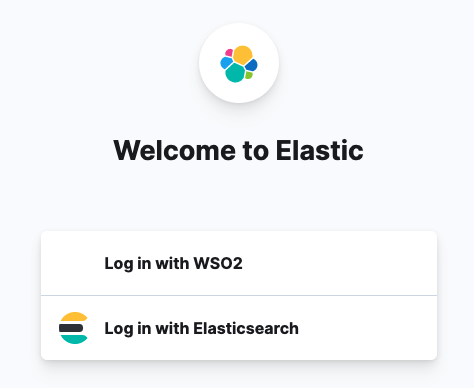
Logout from the Kibana and re-login by selecting the Log in with WSO2 option.
-
This will navigate to the WSO2 API Manager login page. Try login with the previously created user credentials.
Configure SSL/TLS to secure ElasticSearch, Kibana, Beats, and Logstash¶
For more information regarding configuring SSL/TLS to secure ElasticSearch, Kibana, Beats, and Logstash follow the steps mentioned in this article.
Dashboards¶
Analyzing statistics¶
Once you have set up the Kibana dashboards, you can access the following dashboards.
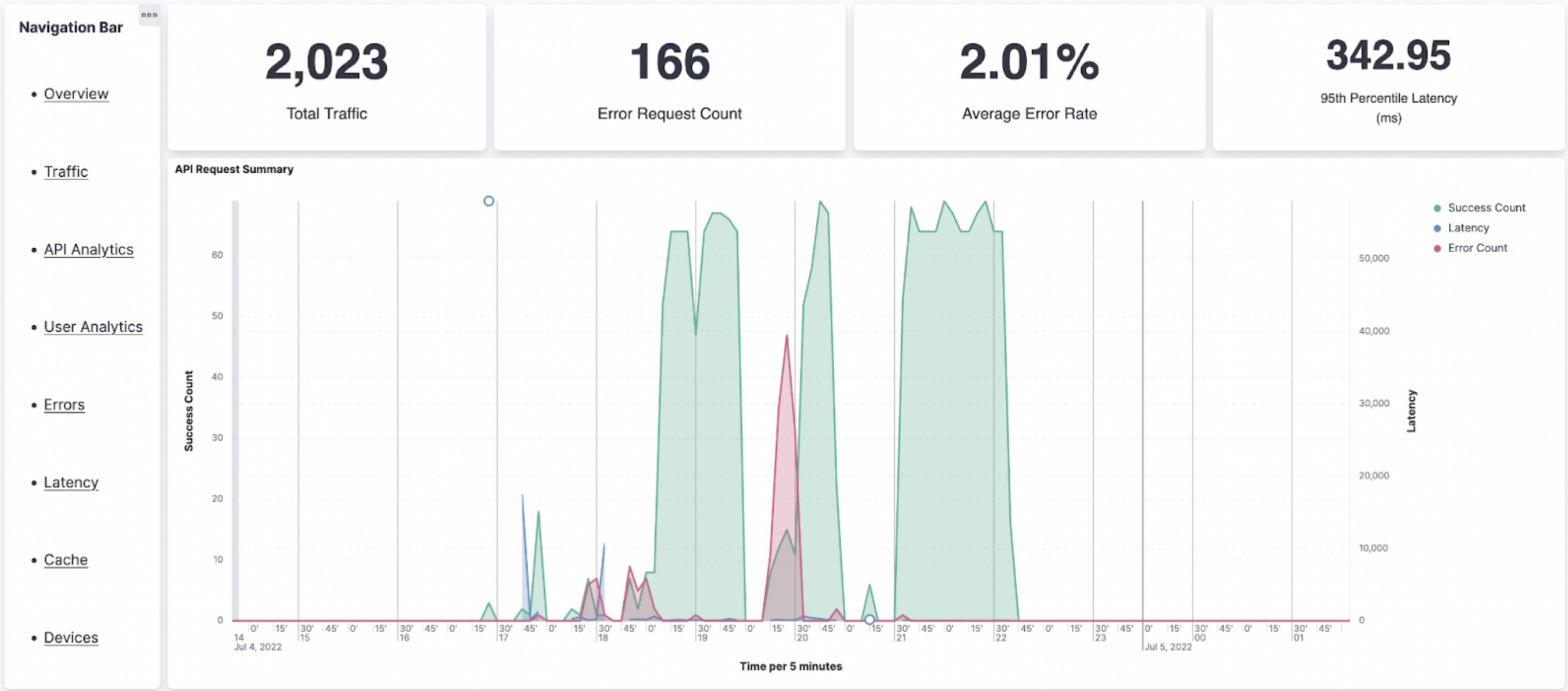
Overview¶
The Overview page gives you a quick overview of the performance of the system. It can be used as a dashboard to view the current system status.
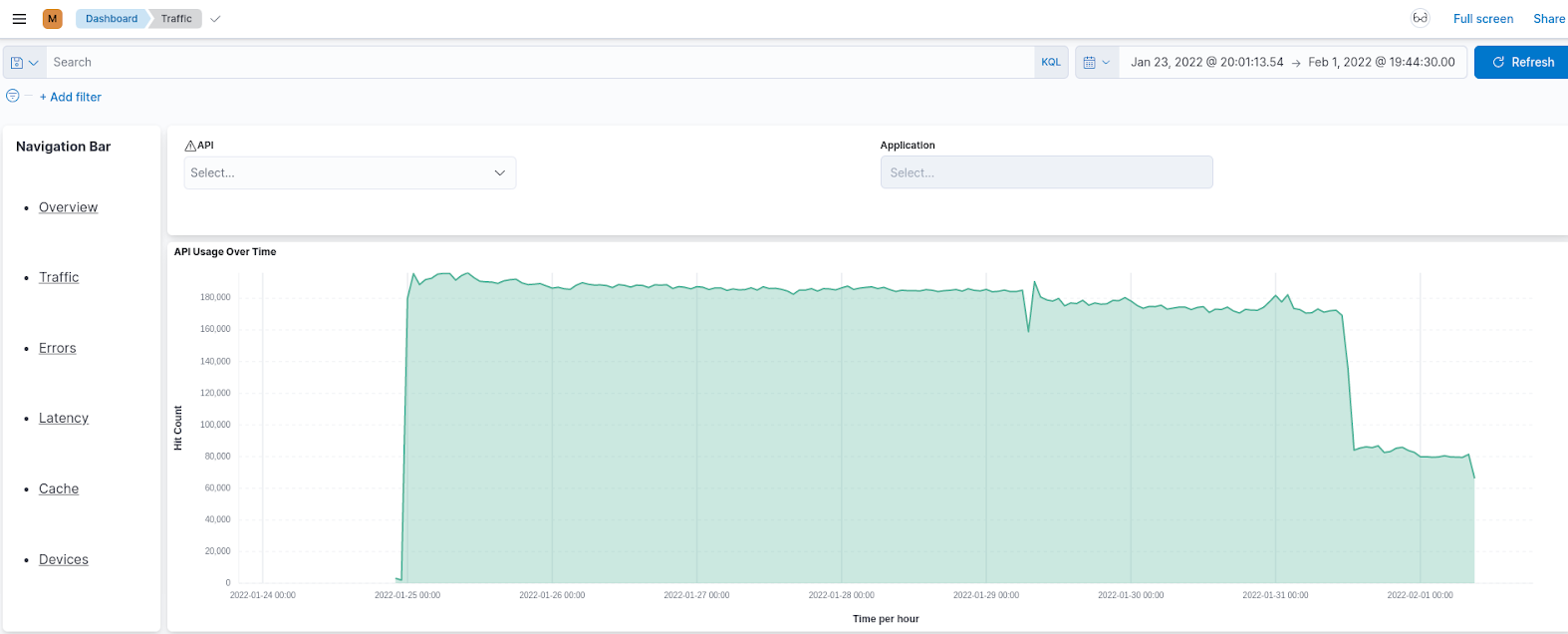
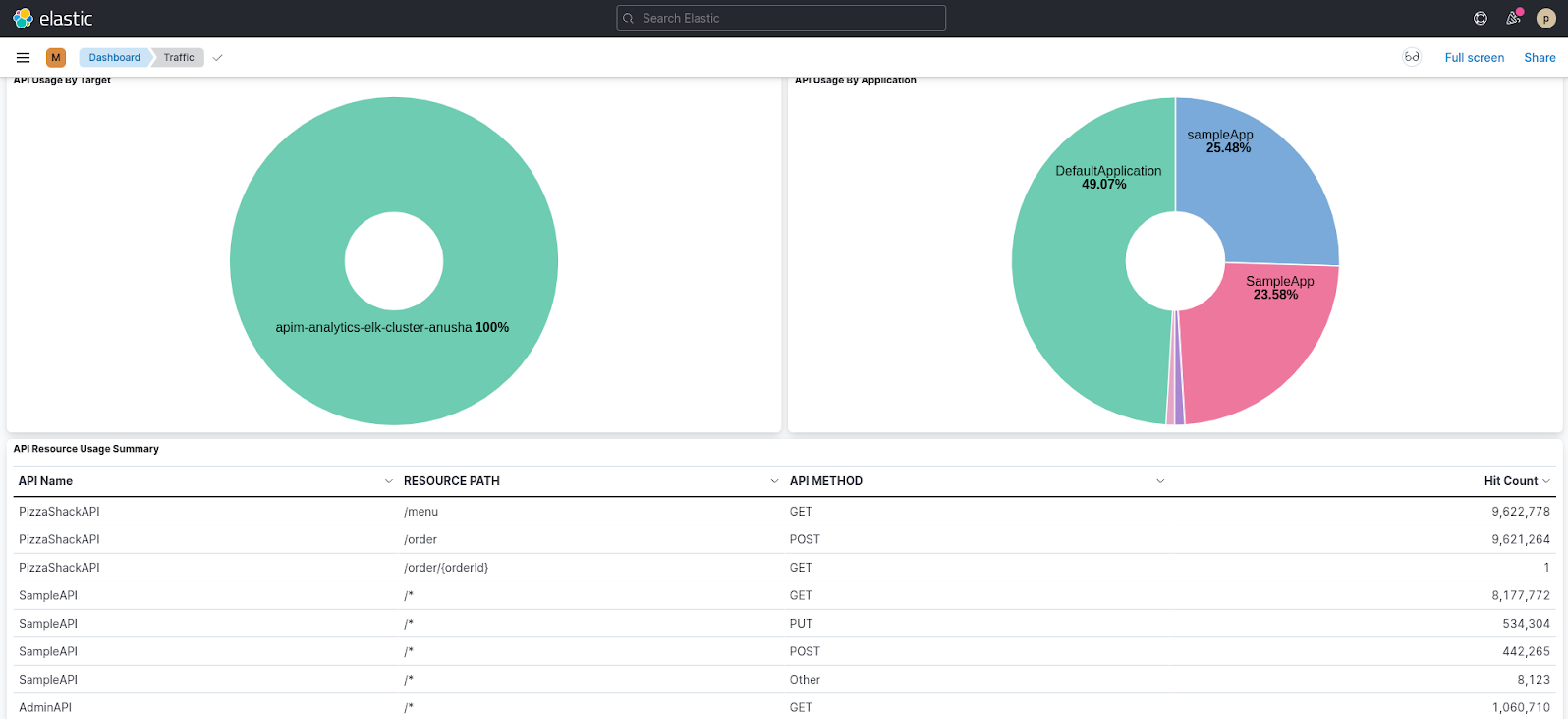
Traffic¶
The Traffic page shows information related to the traffic that goes through your API management deployments. This includes API usage, application usage, resource usage, etc. You can use this page to investigate the usage of APIs and applications, traffic patterns, etc.
API Analytics¶
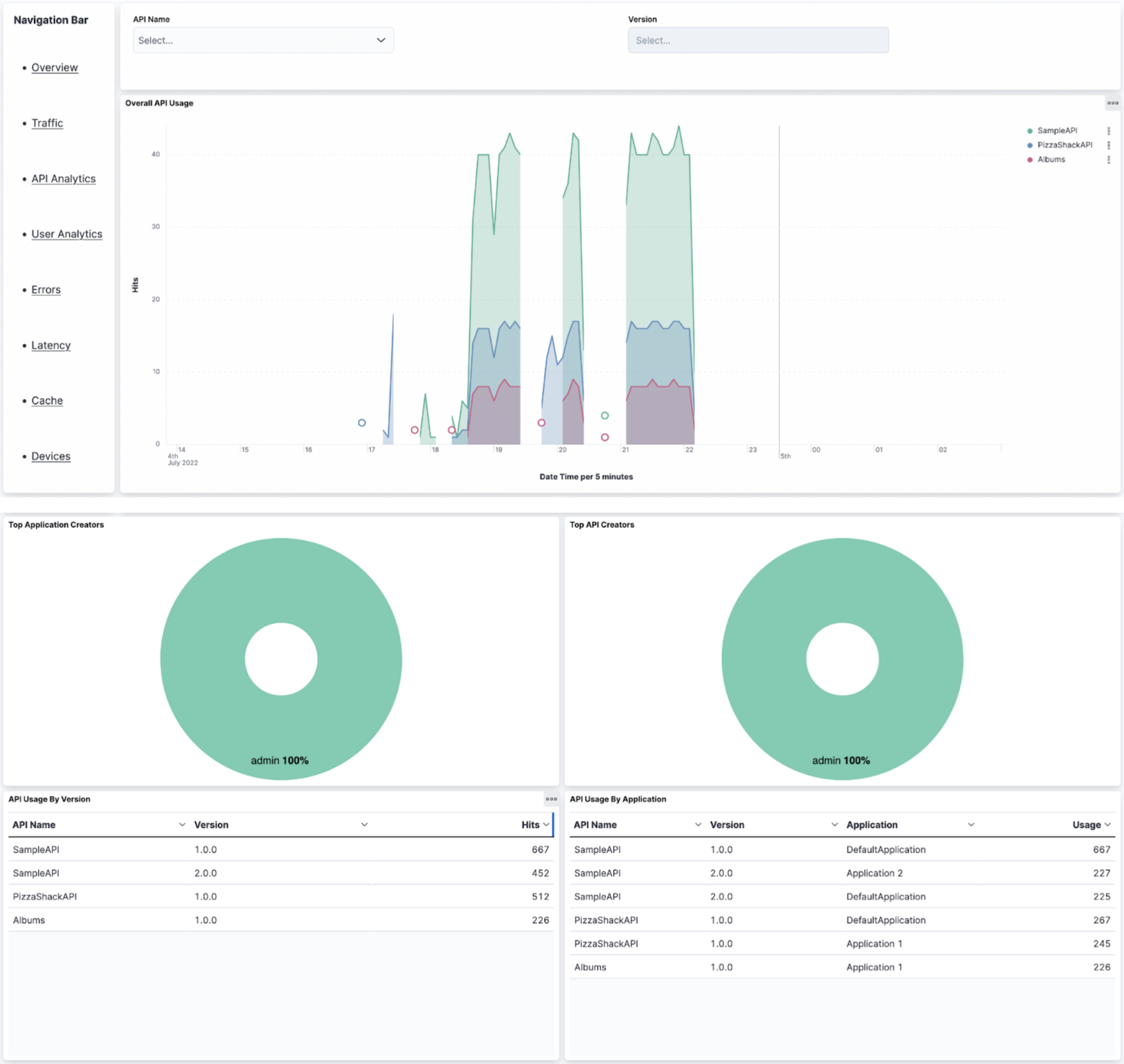
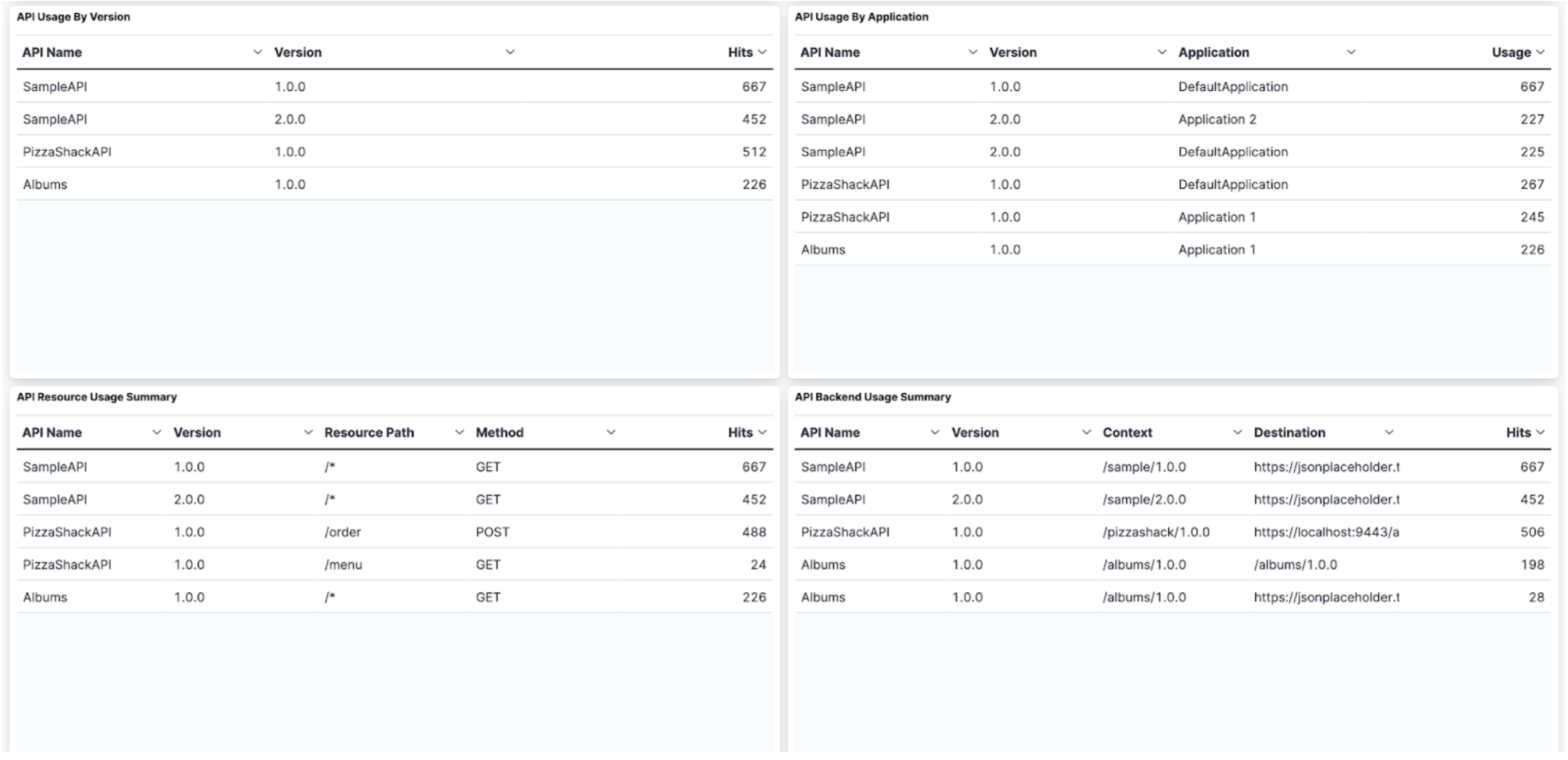
The API Analytics Dashboard provides business insights on APIs enabling users to take proactive actions to improve profitability and the quality of the service provided. This dashboard focuses on API developers who wish to see the analytics related to their APIs. This dashboard includes graphs to represent, Overall API Usage, Top 10 API and Application creators, API Usage by version, application, resource path and backend.
User Analytics¶
User Analytics dashboard provides insights of API Users, most API Users, No of success and fault requests by users for each API and application
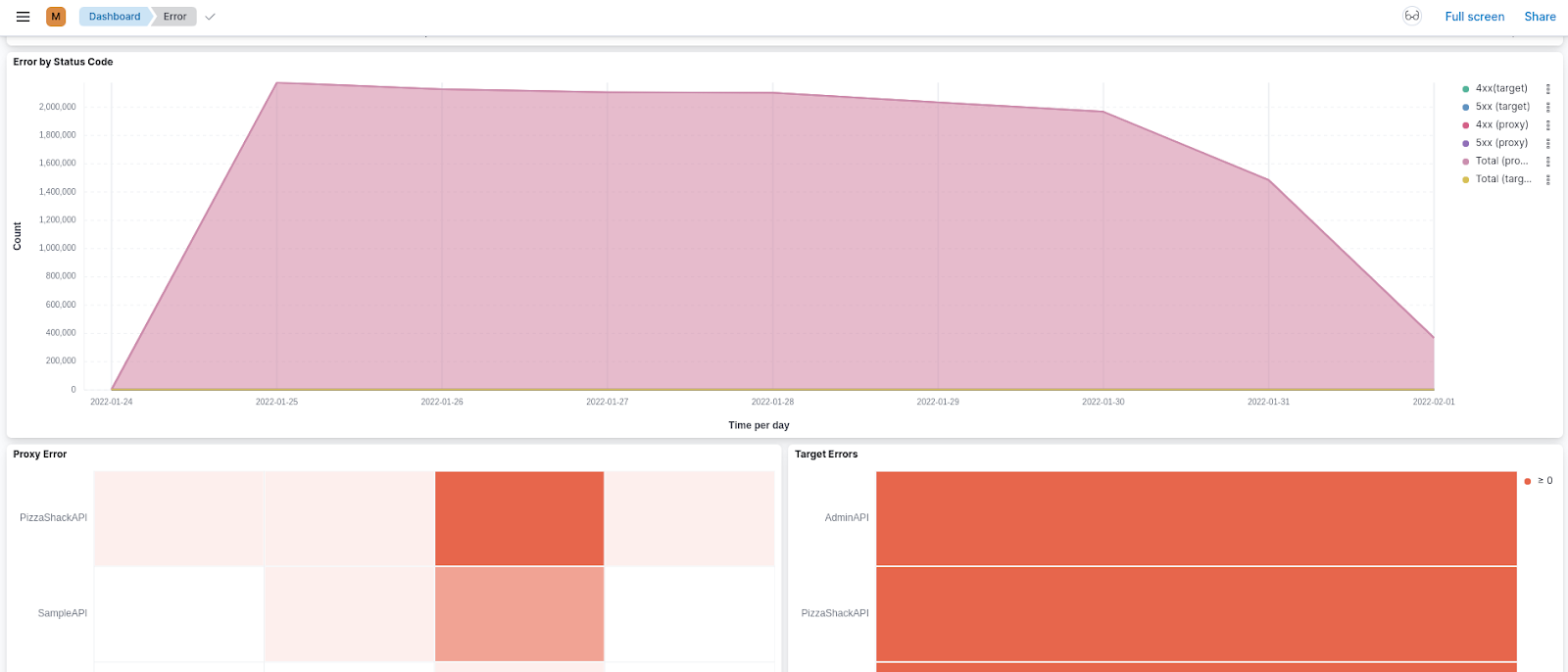
Errors¶
The Errors page shows information related to erroneous API calls that are received by your system. The errors are categorized based on the error type. You can further drill down using the error subtypes. Use this page as the starting point for debugging any API errors.
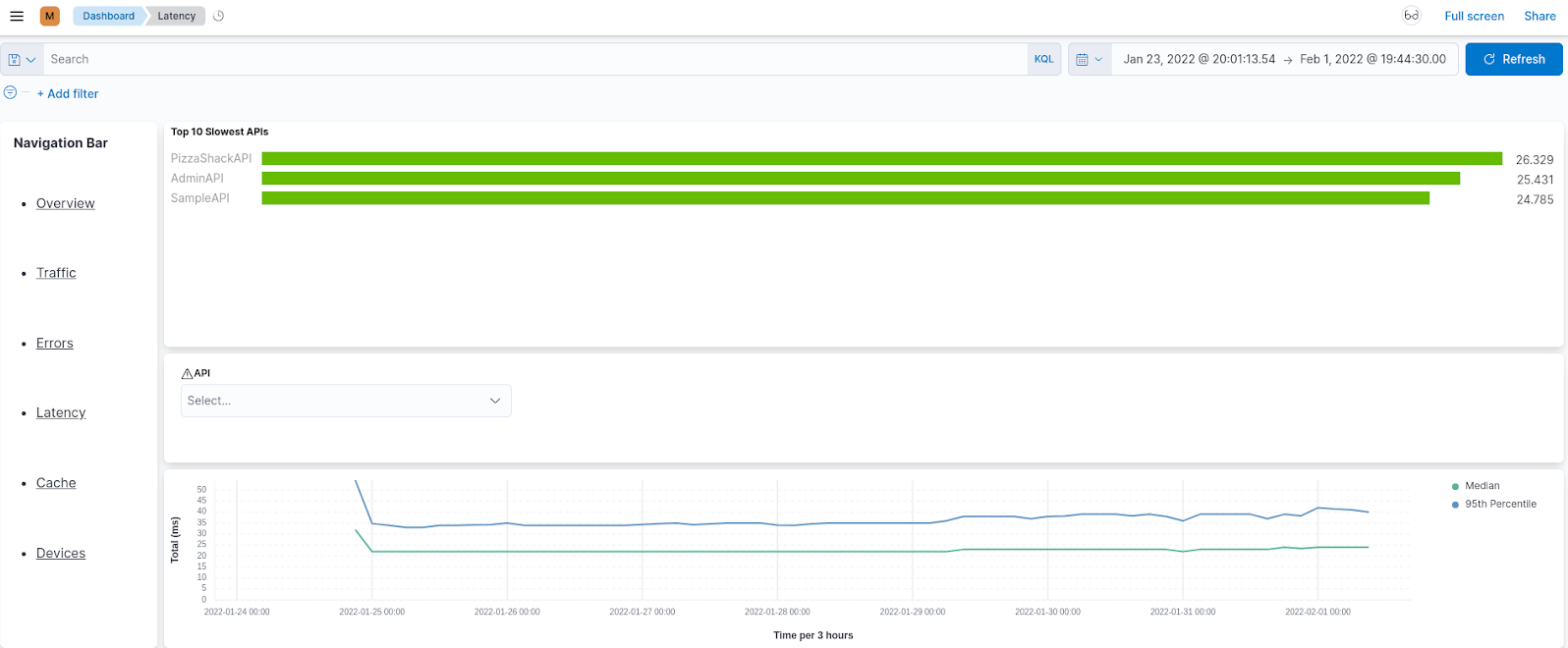
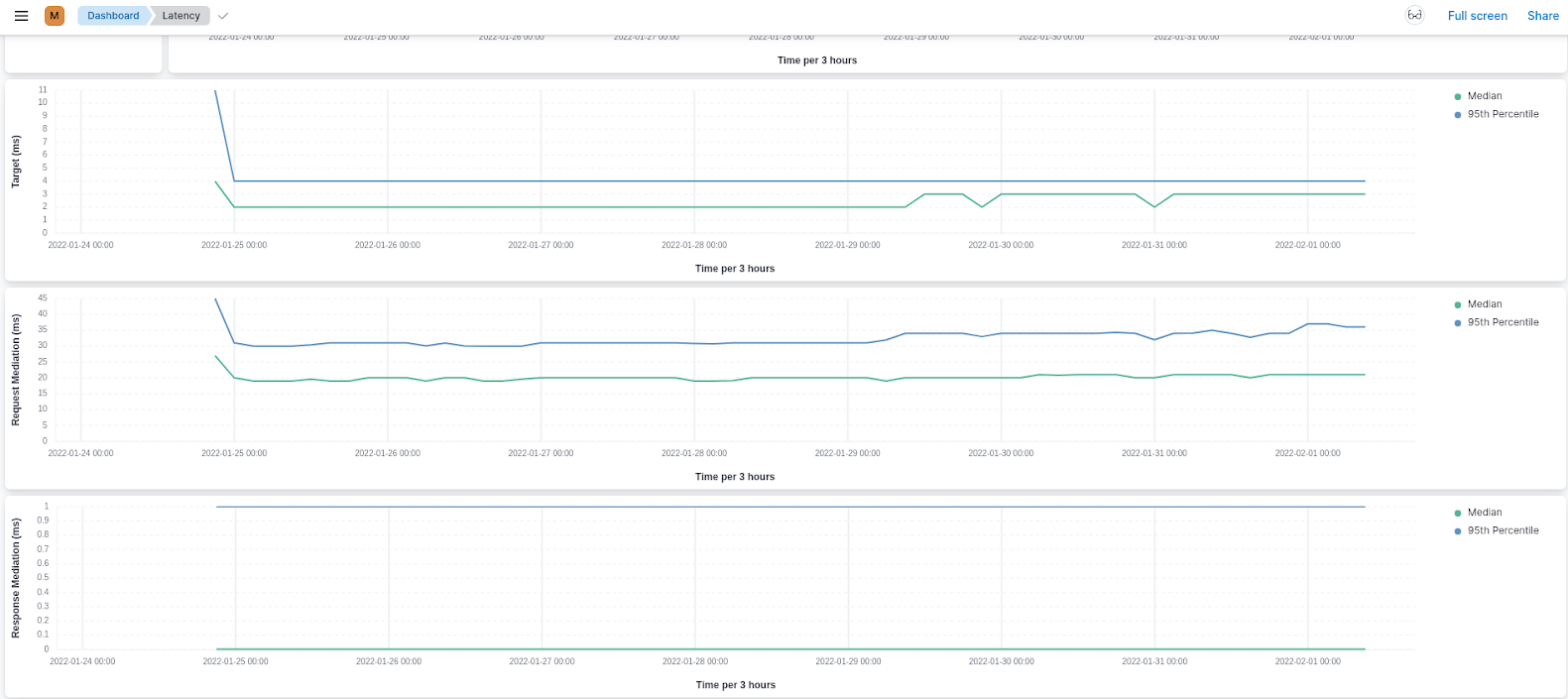
Latency¶
The Latency page shows information related to the latency of API calls within the API management deployment. You can view a summary of the slowest APIs and then drill down into the API view for further analysis. Use this page as a starting point to debug API slowness.
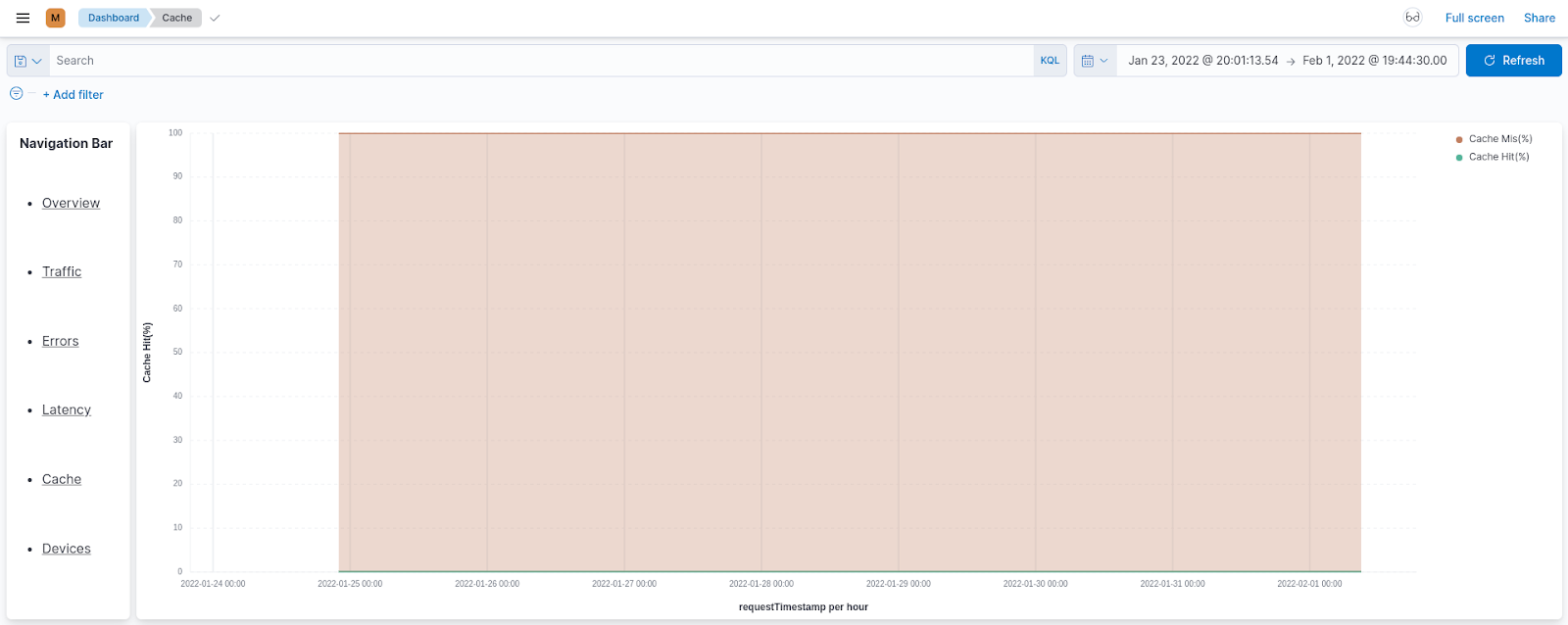
Cache¶
The Cache page shows statistics that indicate the efficiency with which response caching is carried out for the requests sent to your APIs.
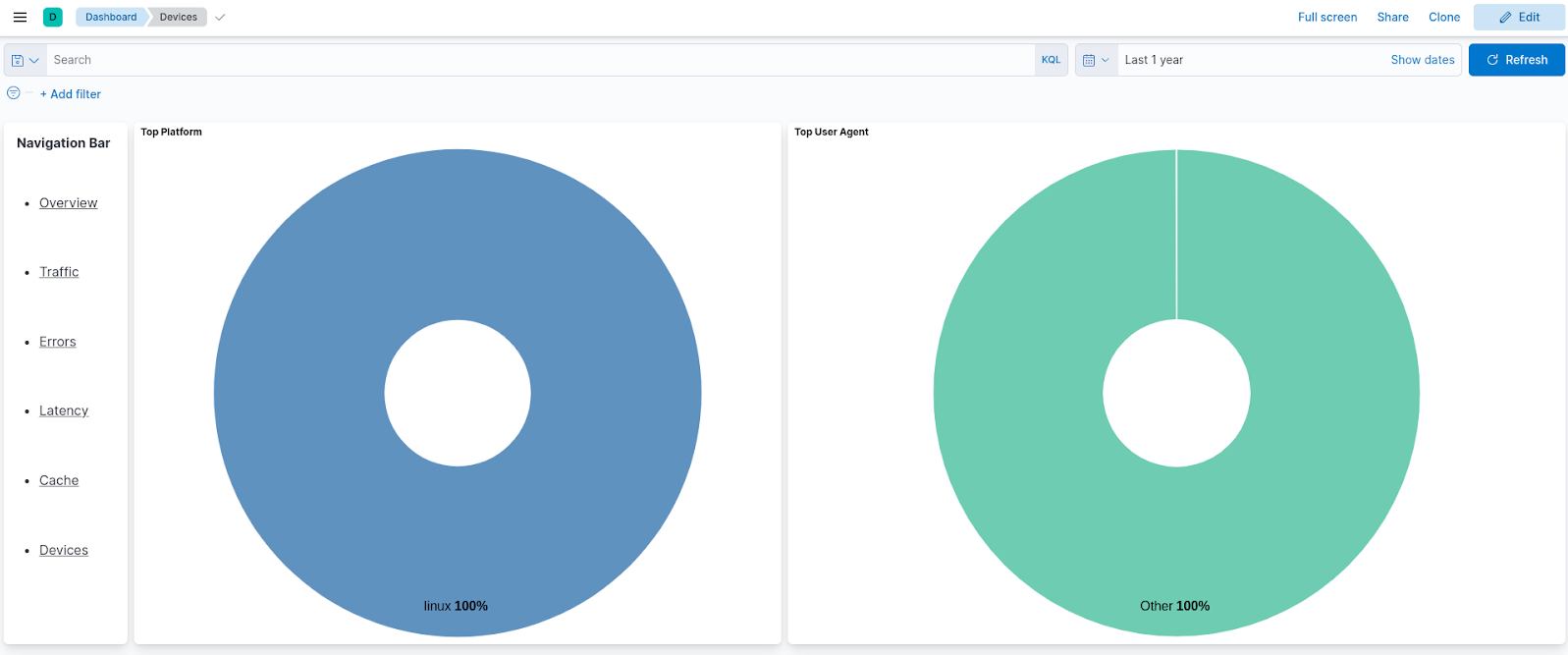
Devices¶
The Devices page displays information about operating systems and HTTP agents that end users use to invoke the APIs. You can use this page to get an idea of the distribution of your user base and improve your APIs to match the audience.