Securing APIs with Mutual SSL¶
In contrast to the usual one-way SSL authentication where a client verifies the identity of the server, in mutual SSL the server validates the identity of the client so that both parties trust each other. This builds a system that has very tight security and avoids any requests made to the client with regard to providing its username/password, as long as the server is aware of the certificates that belong to the client.
The following section explains as to how the APIs in WSO2 API Manager can be secured using mutual SSL in addition to OAuth2.
Create an API secured with Mutual SSL¶
- Create an API.
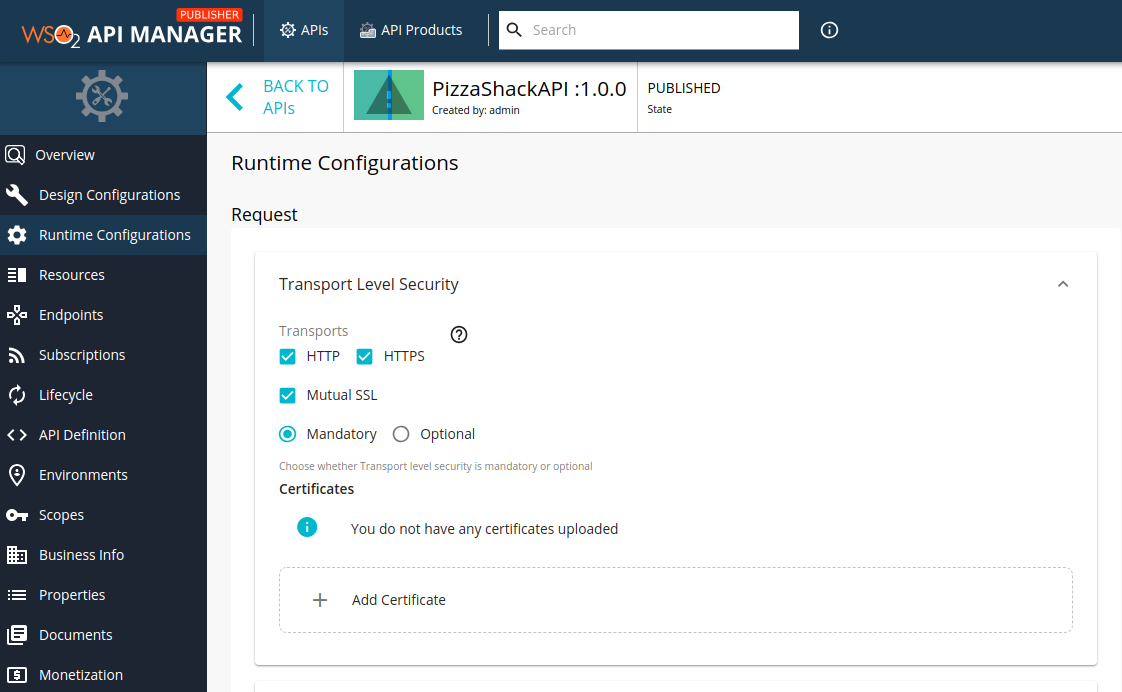
- Click Runtime Configurations.
-
Select Mutual SSL.
-
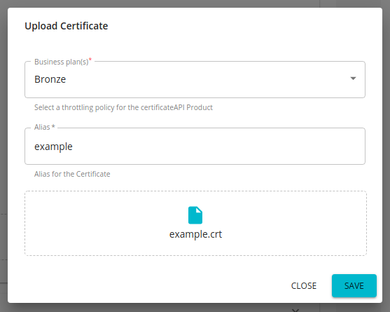
Click Add Certificate to upload a new client certificate.
Note
This feature currently supports only the
.crtformat for certificates.If you need to use a certificate in any other format, you can convert it using a standard tool before uploading it.
-
Provide an alias and public certificate. Select the tier that should be used to throttle out the calls using this particular client certificate and click Upload.
-
Save the API.
Invoke an API secured with Mutual SSL using Postman¶
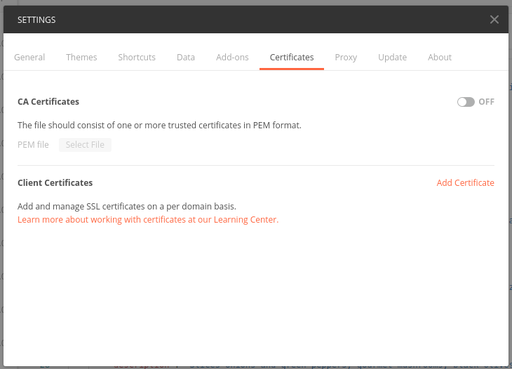
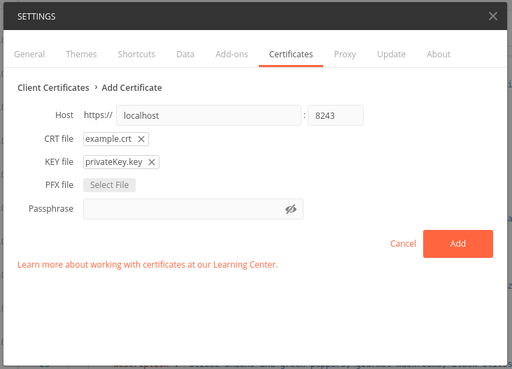
Import the certificate and private key to Postman.
-
Navigate to the certificates tab in Postman settings.
-
Add the certificate and private key.
-
Invoke the API from Postman.
Limitations¶
Listed below are the known limitations for this feature.
-
Application subscription is not permitted for APIs that are only protected with Mutual SSL. Therefore, subscription or application-level throttling is not applicable to these types of APIs.
-
Resource-level throttling is not applicable to the APIs that are only protected with Mutual SSL.
-
Resource-level security will not be applicable to the APIs that are only protected with Mutual SSL.
-
Scope-level security will not be applicable to the APIs that are only protected with Mutual SSL.
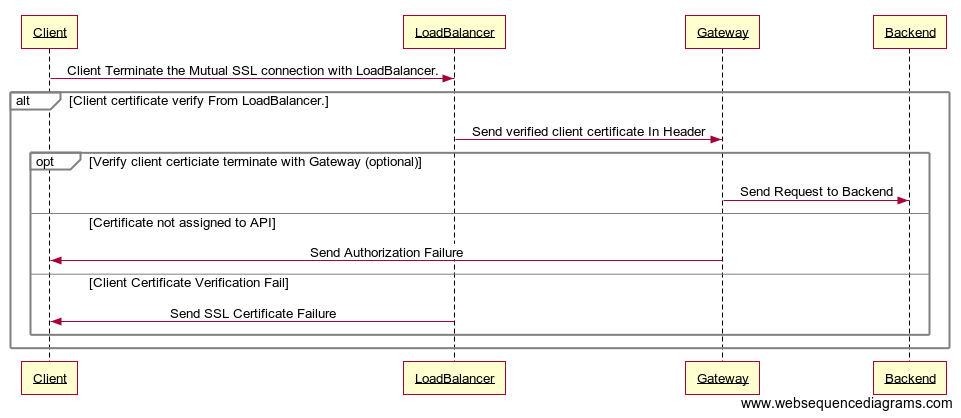
Handling MTLS when SSL is terminated by the Load Balancer or Reverse Proxy¶
When SSL termination of API requests takes place at the Load Balancer or Reverse Proxy, the following prerequisites need to be met by the Load Balancer.
- Terminate the mutual SSL connection from the client.
-
Pass the client SSL certificate to the Gateway in an HTTP Header.
For more information, see the Nginx documentation.
The following diagram illustrates how Mutual SSL works in such an environment.
Using MTLS Header to invoke APIs secured with Mutual SSL¶
By default, the WSO2 API Manager retrieves the client certificate from the X-WSO2-CLIENT-CERTIFICATE HTTP header.
Follow the instructions below to change the header:
- Navigate to the
<API-M_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile. -
Configure the
certificate_headerunder the[apimgt.mutual_ssl]configuration.[apimgt.mutual_ssl] certificate_header = "<Header Name>" # This property needs to be true if the MutualSSL connection is established between the load balancer and the Gateway. enable_client_validation = false #This property needs to be true if the certificate should be decoded when it is passed from the load balancer to the Gateway. client_certificate_encode = false[apimgt.mutual_ssl] certificate_header = "SSL-CLIENT-CERT" enable_client_validation = false -
Start the Server.
-
Invoke the API with the custom header.
curl -k --location -X GET "<API_URL>" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer <access-token>" -H "<MTSL_Header_name>:<Certificate_Key>"curl -k --location -X GET 'https://localhost:8243/test/1.0/foo' -H 'accept: applicaition/json' -H 'Authorization: Bearer 0ee9aa70-d631-3401-b152-521b431036ca' -H 'SSL-CLIENT-CERT: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSURsakNDQW40Q0NRRDc2MUpWekluMGNUQU5CZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJBUXNGQURDQmpERUxNQWtHQTFVRUJoTUMKVTB3eEVEQU9CZ05WQkFnTUIxZGxjM1JsY200eEVEQU9CZ05WQkFjTUIwTnZiRzl0WW04eERUQUxCZ05WQkFvTQpCRmRUVHpJeEN6QUpCZ05WQkFzTUFrTlRNUkl3RUFZRFZRUUREQWxzYjJOaGJHaHZjM1F4S1RBbkJna3Foa2lHCjl3MEJDUUVXR25kaGRHaHpZV3hoYTI5eVlXeGxaMlZBWjIxaGFXd3VZMjl0TUI0WERUSXhNREV4TkRBME16VXoKTlZvWERUSXlNREV4TkRBME16VXpOVm93Z1l3eEN6QUpCZ05WQkFZVEFsTk1NUkF3RGdZRFZRUUlEQWRYWlhOMApaWEp1TVJBd0RnWURWUVFIREFkRGIyeHZiV0p2TVEwd0N3WURWUVFLREFSWFUwOHlNUXN3Q1FZRFZRUUxEQUpEClV6RVNNQkFHQTFVRUF3d0piRzlqWVd4b2IzTjBNU2t3SndZSktvWklodmNOQVFrQkZocDNZWFJvYzJGc1lXdHYKY21Gc1pXZGxRR2R0WVdsc0xtTnZiVENDQVNJd0RRWUpLb1pJaHZjTkFRRUJCUUFEZ2dFUEFEQ0NBUW9DZ2dFQgpBTWMrRjhJblZmMzAwZ2FraTh2QUZ6cUFTSGNQV0xZalQ4dmMwOUs1TzZHRjgzaXpUa2F0UDFtYW1ydWlKL2VRCk1KL2VLVGhJdzR3MWEzS3Y4cjJwc3d2bWRjdjAzZnhRNis2aFh3Ykh5VUtHWFFwbVhtL3d5VE01NzRlR1cybXAKM2toTjlIdFV0SU5uS3BzSENLcFI3MFhGKzNrTTZleHJJNnRJUUpxdTdKM2t1OEdqRVI3R1Vma2trYXI1OGs3eApibEpIWG5URkdjWXJNSXAvcS9YUENqR0pGajhub2tNbjhnL0dWTExCVGFXSWJVa3E2ejRJYjk1dHNOd2thU1dhCnh6U2t3K3JIVkZLWnpPTlV1WTdKTk16Zkp6RkllZG5lY0U3c2Y0WnFIRlF6aUpVbW9qWklDMXp5bFdZdzQ4OEUKNUZvaU9xTWpHYTlUMXhXMUpOWTBab01DQXdFQUFUQU5CZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJBUXNGQUFPQ0FRRUFSZTdrcWZlbwpjd1htazRLWlBKMmlnaGY2VU9jc2dYSEZqMnVpQTNhSWMrd2xwREJpdkdCbDJHM2gxQXl6UFNtcVpYaUcvTGttCkg1dm43VUpGQXlQRVBlQ25HdWduTk5kZGpnSFp0SEdJLzdXcm1LTHdIOEU3TWdmSWJ6dk5Hd3ZXWmRrZi9DblcKNjNDYzhhTzJQMDhYd0dHU25JSDg2cWF6NEtvZUF1aFlCdHZyekNObERraTFjZ1E1bHczU0djU3dxMlB0eEd4cApvS0xWOUJYUzlVdUNJRDRrYjFqRUo3YlplTis0Z0pDbTVGTldUbWdhWXFDcjdERWIwRkhpWitLVnBsZzJZZ3ZYCkM2Z2ZrRm9NYTVJREwvWGVja0J0dFlITzFKcWUyMElRKy9kVHB4ZWE4RjE5aDVmeDRZWVlsRFhLWS8wRmxiRXoKZ1l2UGFIUnVKWnFlV1E9PQotLS0tLUVORCBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCg=='
Note
The MTLS flow described above uses the Nginx load balancer. When using a different ELB to configure the MTSL with SSL termination, refer the service provider's documentation and feature catalog to do the necessary configurations.