Using Dynamic Data in API Controller Projects¶
The API Controller (CTL) can inject dynamic values based on environment variables to various project files. The use of environment variables is a very convenient way of controlling inputs in almost every CI/CD platform.
Initialize API Projects with Dynamic Data¶
When initializing an API Project, the CTL is capable of detecting environment variables in the default definition file or in the provided custom definition file. Then it will create the primary API configuration file api.yaml with the dynamic data based on the environment variables. When executing the apictl init command, the CTL automatically injects the values to the API definition. You can use the notations $ENV_VAR or ${ENV_VAR} to specify environment variables to any attribute in this file.
Follow the instructions below to initialize an API Project with environment variables.
-
Create a file
api-env-config.yamlwith the below content.id: apiName: $APINAME version: $APIVERSION context: /petstore/$APIVERSION contextTemplate: /petstore/{version} -
Export the environment variables with required values.
export APINAME=Petstore export APIVERSION=1.0.0SET APINAME=Petstore SET APIVERSION=1.0.0 -
Initialize the API Project with the api-env-config.yaml
apictl init PetstoreProject -d api-env-config.yaml --oas https://petstore.swagger.io/v2/swagger.jsonTip
Upon successful completion of the above command, the CTL will automatically inject the environment variable values to the API artifact in the API project. Open
PetstoreProject/Meta-information/api.yamland check the above values are correctly injected.id: providerName: admin apiName: Petstore version: 1.0.0 description: 'This is a sample server Petstore server. You can find out more ..' type: HTTP context: /petstore/1.0.0 contextTemplate: /petstore/{version} ...Now you can import the Project using
import-apicommand. -
Import the API
apictl import-api -f PetstoreProject -e developmentWarning
If an environment variable is not set, the command will fail and request a set of required environment variables on the system.
Once the project is successfully imported, sign-in to the WSO2 API Publisher and check the newly imported API with the same details specified above.
Add Dynamic Data to Environment Configs¶
To allow easily configuring environment-specific details, by default, the CTL supports an additional parameter file named api_params.yaml. For more information on using an environment parameter file, see Configuring Environment Specific Parameters.
The file supports detecting environment variables during the API import process. You can use the notations url: $DEV_URL or url: ${DEV_URL} to specify environment variables to any attribute in this file.
-
Create a file
api_params.yamlwith the below content.environments: - name: development endpoints: production: url: $DEV_ENV_PROD_URL config: retryTimeOut: $DEV_ENV_PROD_RE_DELAY retryDelay: $DEV_ENV_PROD_RE_TO sandbox: url: $DEV_ENV_SAND_URL -
Export the environment variables with required values.
export DEV_ENV_PROD_URL=https://petstore.swagger.io/v2 export DEV_ENV_PROD_RE_DELAY=10 export DEV_ENV_PROD_RE_TO=5 export DEV_ENV_SAND_URL=https://sand.petstore.swagger.io/v2SET DEV_ENV_PROD_URL=https://petstore.swagger.io/v2 SET DEV_ENV_PROD_RE_DELAY=10 SET DEV_ENV_PROD_RE_TO=5 SET DEV_ENV_SAND_URL=https://sand.petstore.swagger.io/v2 -
Import the API Project
apictl import-api -f PetstoreProject --environment development --params PetstoreProject/api_params.yaml --updateWarning
If an environment variable is not set, the command will fail and request a set of required environment variables on the system.
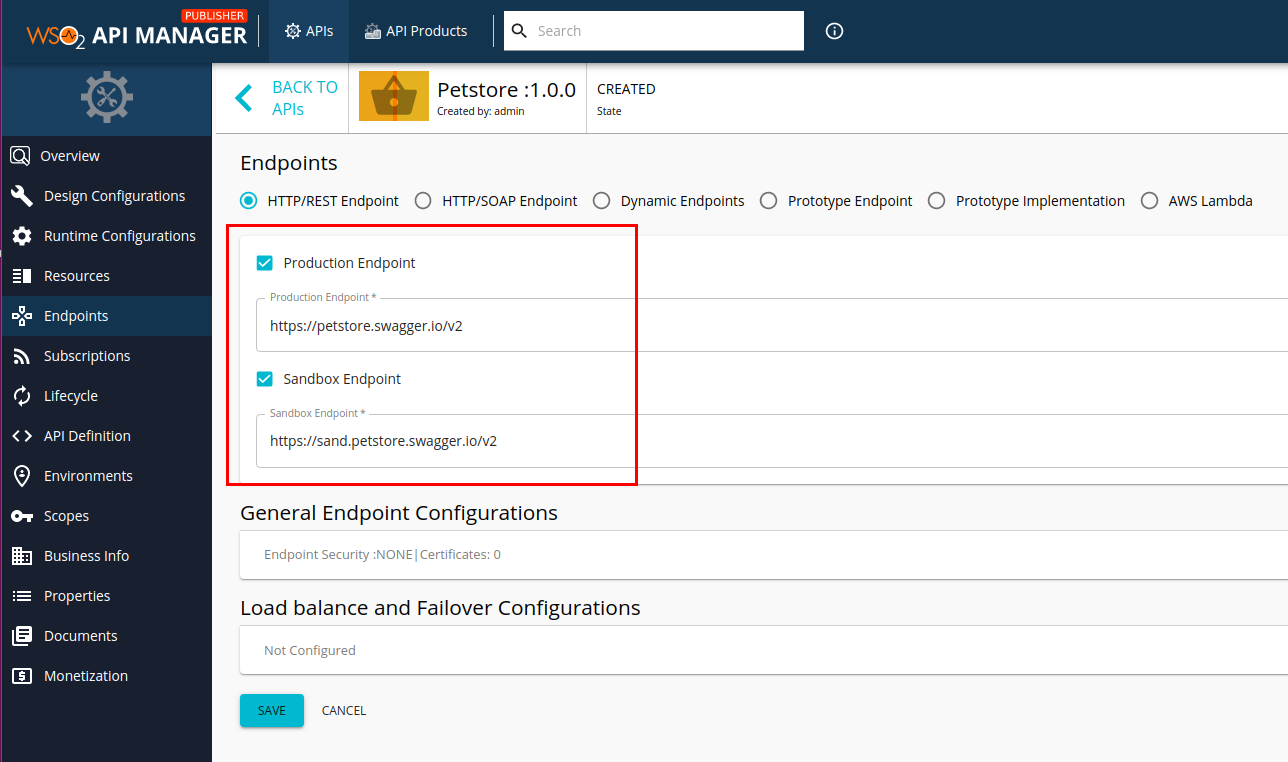
Once the project is successfully imported, sign-in to the WSO2 API Publisher and check the Endpoints section of the imported API. The URLs specified as environment variables will appear there.
Add Dynamic Data to other files in an API Project¶
Other than the default API Definition (api.yaml) and API's Environment Configuration (api_params.yaml), the CTL supports environment variable substitution in other project files including documents, custom mediation policies and SOAP-to-REST conversion policies.
Note
Only ${ENV_VAR} notation is supported to specify environment variables in these types of files.
For example, consider we need to send a special header to the backend when calling the Petstore API we created above. The value of the header should be a dynamic value which the CTL should have control over.
-
Create the below custom mediation policy
custom-header-in.xmlinPetstoreProject/Sequences/in-sequence/Customfolder.<sequence xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse" name="custom-header-in"> <header name="X-ENV-KEY" value="${ENV_KEY}" scope="transport" /> <log level="custom"> <property name="Sent header(X-ENV-KEY)" value="${ENV_KEY}"/> </log> </sequence> -
Open
PetstoreProject/Meta-information/api.yamland change below settings.- Replace
statusvalue fromCREATEDtoPUBLISHED. This is to ensure that the API will be Published once imported. - Add
inSequence: custom-header-in
A sample configuration after applying the above changes is shown below.
id: providerName: admin apiName: Petstore version: 1.0.0 description: 'This is a sample server Petstore server...' type: HTTP context: /petstore/1.0.0 contextTemplate: /petstore/{version} inSequence: custom-header-in status: PUBLISHED ... - Replace
-
Export the environment variables with required values.
export ENV_KEY=dev_101SET ENV_KEY=dev_101 -
Import the API Project
apictl import-api -f PetstoreProject --environment development --params PetstoreProject/api_params.yaml --update -
Generate a token and invoke the API
$ apictl get-keys -e dev -n Petstore -v 1.0.0 -r admin eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUz....RWrACAUNSFBpxz1lRLqFlDiaVJAg $ curl -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUz....RWrACAUNSFBpxz1lRLqFlDiaVJAg" https://localhost:8243/petstore/1.0.0/pet/1 -k {"id":1,"category":{"id":1001,"name":"Animal"},"name":"doggie","photoUrls":["img/test/dog.jpeg","img/test/dog1.jpeg"],"tags":[{"id":2001,"name":"Pet"},{"id":2002,"name":"Animal"}],"status":"available"}
Upon successful invocation, the header X-ENV-KEY: dev_101 will be sent to the backend of the API. The below log will be printed in the API gateway's terminal.
INFO - LogMediator Sent header(X-ENV-KEY) = dev_101