Synchronizing Artifacts in a Gateway Cluster¶
In an API-M Gateway cluster, artifact synchronization is critical to maintain consistency among the nodes. WSO2 API-M provides three mechanisms for artifact synchronization.
Artifact synchronization with a shared file system¶
To enable synchronization for runtime artifacts of two all-in-one WSO2 API-M instances, it is recommended to have a shared file system. Configure a shared file system as the content synchronization mechanism. You can use a common shared file system such as Network File System (NFS) or any other shared file system that is available.
You need to mount the following directories of the two nodes to the shared file system, in order to share all the APIs and throttling policies between all the nodes.
<API-M_HOME>/repository/deployment/server/synapse-configs<API-M_HOME>/repository/deployment/server/executionplans
Inbuilt artifact synchronization¶
Overview¶
Currently, in a multi-gateway environment, Synapse artifacts such as API synapse definitions, sequences, local entries, and endpoints are saved in the <API-M_HOME>/repository/deployment/server/synapse-configs/default directory as XMLs. These artifacts have to be synced between all the Gateway nodes using an artifact synchronizing mechanism such as NFS or Rsync.
When using NFS, you need to manage additional components that bring in changes to the current architecture. Therefore, an inbuilt artifact synchronization solution has been introduced. This inbuilt Artifact Synchronizer can be configured to store these Synapse artifacts to an extension point (configured persistent storage).
The behaviour of the inbuilt Artifact Synchronizer in different scenarios is described as follows.
Artifact synchronization when the API Gateway is running¶
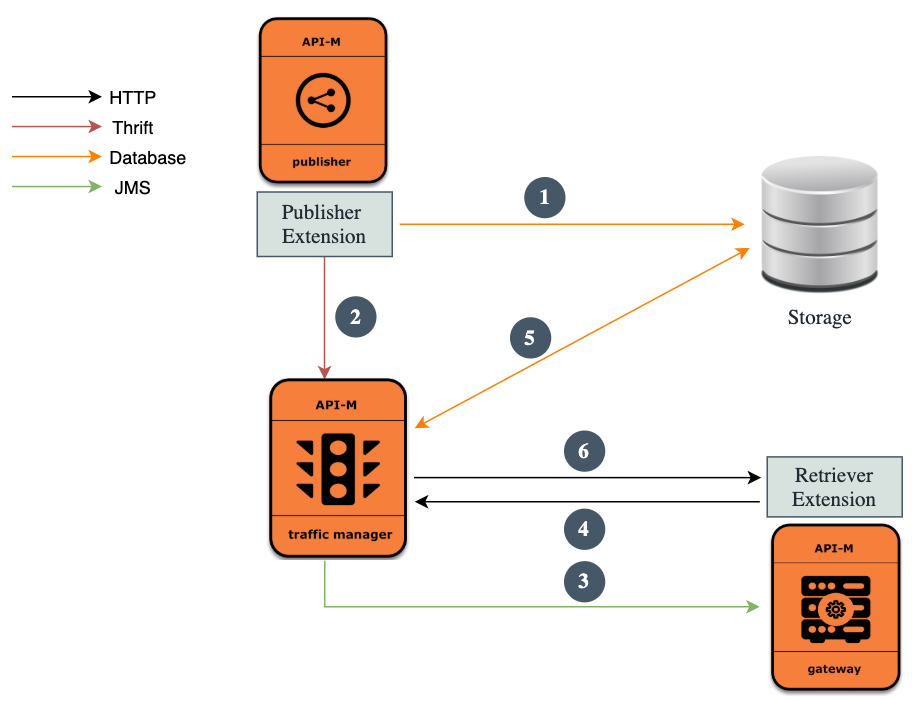
- If an API is published, edited, or removed, the Synapse artifact corresponding to the API will be stored/updated in the storage through the configured extension point.
- An event will be sent to Traffic Manager (TM) using event notifiers with the API Name, UUID, and the Gateway label of the API.
- In a distributed deployment, Gateways are subscribed to the Traffic Manager. The API Gateway will filter out the events by the Gateway label.
- The Gateway will request for the artifacts related to the event received from the Traffic Manager.
- Traffic Manager will connect to the database and fetch the artifacts.
- The Gateway will receive the artifacts and deploy. If the API is already deployed in the Gateway, it will first undeploy the API and redeploy with the retrieved artifacts.
Artifact synchronization at API Gateway startup¶
At startup, the Gateway will look for the APIs with labels that it is subscribed to in the configured extension, and fetch the Synapse artifacts of those APIs. Those Synapse artifacts will get deployed in the Gateway.
Gateways are subscribed to the Traffic Manager. There is an extension in the Gateway to get the Synapse artifacts and deploy them in the memory. Gateways can subscribe to multiple labels.
Gateway Labels and Environments¶
If you need to deploy an API in a specific Gateway, you could use either Gateway Labels or Gateway Environments to expose that particular Gateway.
Configuring the Inbuilt Artifact Synchronizer¶
Configure the Gateway and Publisher profiles as explained below to enable artifact synchronization and retrieval from configured extension points.
Publisher profile configurations¶
- Stop the Publisher node if it is running.
-
Open the
<API-M_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile and update it as follows:[apim.sync_runtime_artifacts.publisher] artifact_saver = "DBSaver" publish_directly_to_gateway = "false"Configuration Description apim.sync_runtime_artifacts.publisher The configuration element that all the artifacts will be saved to the storage via the extension point. By default, they will get stored in the database. artifact_saver Specify the extension point. The default is DBSaverwhere the artifacts are saved in the database.publish_directly_to_gateway If publish_directly_to_gateway = true, then the artifacts will be published to the Gateway directly. Ifpublish_directly_to_gateway = false, then the Published API details will be notified to the Traffic Manager through events.
Info
publish_directly_to_gateway parameter is introduced to preserve the previous Gateway Environment experience. In previous versions, to deploy the Gateway runtime artifacts, Publisher portal directly invokes the Gateway admin service (given as server url) with the deployment artifacts.
Once we enable the Inbuilt Artifact Syncronizer, if publish_directly_to_gateway = false is given, even for the gateways exposed in Publisher as Gateway Environments will have to subscribe to the Gateway Label (Environment name) and will wait until the Traffic Manager event to pull the artifact.
Gateway profile configurations¶
- Stop the Gateway node(s) if it is running.
-
Open the
<API-M_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.tomlfile and update it as follows:[apim.sync_runtime_artifacts.gateway] gateway_labels =["Production and Sandbox","Label1","Label2"] artifact_retriever = "DBRetriever" deployment_retry_duration = 15000 max_retry_count = 5 data_retrieval_mode = "async" event_waiting_time = 5000Configuration Description gateway_labels Specify the labels that the Gateway is going to subscribe to. Only the APIs with these labels will be pulled from the extension point and deployed. artifact_retriever Specify the extension point. The default is DBRetrieverwhere the artifacts are pulled from the database.deployment_retry_duration Specify the retry duration in milliseconds to deploy artifacts if there is a failure in pulling them from the extension through deployment_retry_duration. The retry duration specified here will be exponentially increased by a progression factor of 2. Thereby, the duration will be progressed as 15s, 30s, 60s, 120s and so on if there are continuous failures. The retry duration is bounded by 1 hr.Note
This
deployment_retry_durationis applicable only in Asynchronous deployment (data_retrieval_mode ="async") where the server will try to deploy the artifacts after it is started.max_retry_count Specify the maximum number of retries for retrieving and deploying artifacts in case of a failure. The default max_retry_countis set to5.data_retrieval_mode You can use the data_retrieval_modeelement to specify the mode of deployment of artifacts from the extension point. The gateway Startup will change based on the mode that is selected (syncorasync) and if there are any failures in the deployment process, it will be triggered again for "n" times where "n" is the maximum retry count. If the APIs are not deployed even in "n" retries, then the server will start with undeployed API artifacts. In the Asynchronous mode, the server will be up and independent of the deployment of the Synapse artifacts in the Gateway. In the Synchronous mode, the server will wait until all the APIs have been deployed.Note
If you have set
data_retrieval_modetosync, you cannot perform lazy loading for tenants successfully. Therefore, setdata_retrieval_modetoasyncto enable lazy loading for tenants.event_waiting_time You can use this element to specify an event waiting time in milliseconds (ms) for Gateway. The Gateway will wait for the time specified in this configuration after receiving an event. This ensures that artifact retrieval is not ahead of artifact updates in the Publisher; thereby, avoiding inconsistencies. The default waiting time will be 1 ms.
Retrieve artifacts from the storage¶
Once the Inbuilt Artifact Synchronizer is enabled, runtime artifacts will no longer be saved to the file system (<API-M_HOME>/repository/deployment/server/synapse-configs/default directory as XMLs). Instead they will be saved as blobs in the database.
However, for debugging purposes or recovery purposes, you can use the Gateway REST API to view artifacts, redeploy artifacts or undeploy artifacts.
Note
Please note that Gateway REST API operations are local to that Gateway deployment. If there are multiple Gateway nodes in the cluster, undeploying the artifacts with the REST API resource in one Gateway node will not undeploy from the entire cluster.
Tip
Even though the artifacts are not getting saved to the file system, if we add a valid XML with the relevant runtime artifacts (retrieved from the Gateway REST API) to the <API-M_HOME>/repository/deployment/server/synapse-configs/default/api directory,
it will undeploy the current artifact and deploy the API from the file system. This can be used to debug the behavior of the artifact. However this is not recommended as it can cause inconsistencies in the runtime artifacts.
Database configurations¶
By default, the data related to the Synapse artifacts will be stored in the WSO2AM_DB. However, this is configurable.
Follow the instructions below to configure a database to store the Synapse artifacts.
Note
Only the data related to the Synapse artifacts will be saved in this database.
Add the [database.sync_runtime_artifacts_db] configuration element and thereafter, update the URL pointing to your database, the username, and password required to access the database and the driver details as shown below.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| type | The database type used. |
| url | The URL of the database. The default port for MySQL is 3306. |
| username and password | The name and password of the database user. |
| driverClassName | The class name of the database driver. |
The following sample configuration is for MySQL. If you are using any other database, update the type and URL accordingly.
[database.sync_runtime_artifacts_db]
type = "mysql"
url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/<DATABASE_NAME>"
username = "<USER_NAME>"
password = "<PASSWORD>"[database.sync_runtime_artifacts_db]
type = "mysql"
url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/WSO2AS_DB"
username = "wso2carbon"
password = "wso2carbon"Info
For more information on the other parameters that can be defined in the
<API-M_HOME>/repository/conf/deployment.toml file, see Tomcat JDBC connection pool.
Add the tables of the AM_GW_API_ARTIFACTS and AM_GW_PUBLISHED_API_DETAILS to this new database that you are specifying.
The scripts to create these tables are in the <API-M_HOME>/dbscripts/apimgt/ directory.
FAQ About Inbuilt Artifact Synchronizer¶
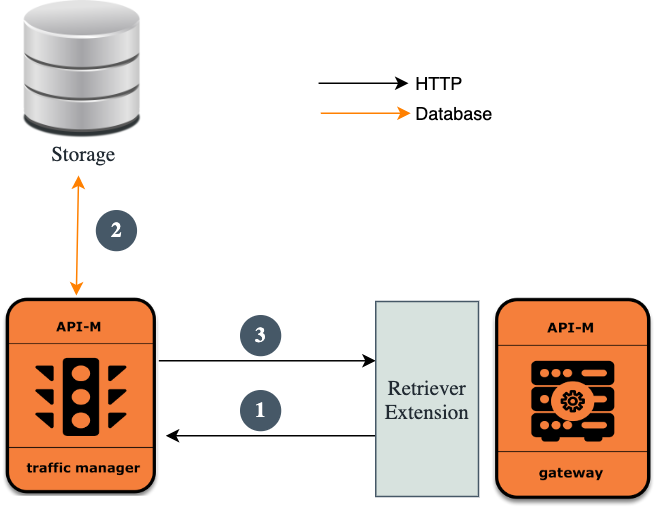
In this architecture, does the Gateway require a database connection? No. Gateway does not need to connect with the database to pull the artifacts. It requests from the Traffic Manager and Traffic Manager connects with the database. In this architecture Traffic Manager plays a vital role and maintains the connections with the database.
If the first request (i.e., saving artifacts to DB) failed and the second request (i.e., events to TM) succeeded, what will happen? This will not happen as the event to the Traffic Manager with the published Gateway label will only be sent after a successful DB update. The second request will not be sent if the first step fails.
If the first two requests succeed but third request fails in between, whats sort of recovery procedure TM would follow to make sure Gateways received all the events? Since we are sending the events through JMS topics, it is guaranteed that the events will be received by the Gateway if it is subscribed. Since JMS guarantees the delivery of the message, we have not implemented a recovery procedure during these steps. However if the Gateway is down and could not receive the event, next startup will sync with the database, pull the latest artifacts and deploy.
If the first three requests succeed and the fourth fails indefinitely, and whats the immediate recovery option? If forth request fails, the received event will not deploy or undeploy the API in the Gateway. You can use the Gateway Rest API to redeploy the artifact in the Gateway node. Restarting the server will also resolve all the missing events and update the Gateway status to the latest.
How are the Traffic Manager execution plans handled in this version? Does the DBSaver/DBRetriever handle Traffic Manager or ESB artifacts? In APIM 3.2.0, we only support the Gateway Runtime Artifacts (Synapse Configurations). Execution plan support is provided in APIM 4.0.0 version.
Suppose all the above artifact are to be saved/retrieved from DB instead of file system by Gateway. During API Consumption if DB is not working, will the Gateway fail? No. Gateway will store all the artifacts in memory once it deploys an API. Database connection is required only if the artifact is updated or undeployed. If DB is not working, latest change to API will not get affect. However previous state of the API will preserve in the Gateway and function as it was before.
When there are multiple TM nodes across DCs and a certain TM is receiving the notification of an API publishing from Publisher. However the DB is not updated yet via replication. What would happen?
In such cases, we can add a delay between the request 3 and 4. You can configure this delay with event_waiting_time configuration in Gateway profile.
There is a call going to "internel/data/v1" URL. What is that? This is the internal REST API deployed in TM node. Gateway use this API to request artifacts from the TM.
Top