Understanding the Distributed Deployment of WSO2 API-M¶
Before understanding how to deploy WSO2 API Manager (WSO2 API-M), let's understand the WSO2 API-M distributed deployment better.
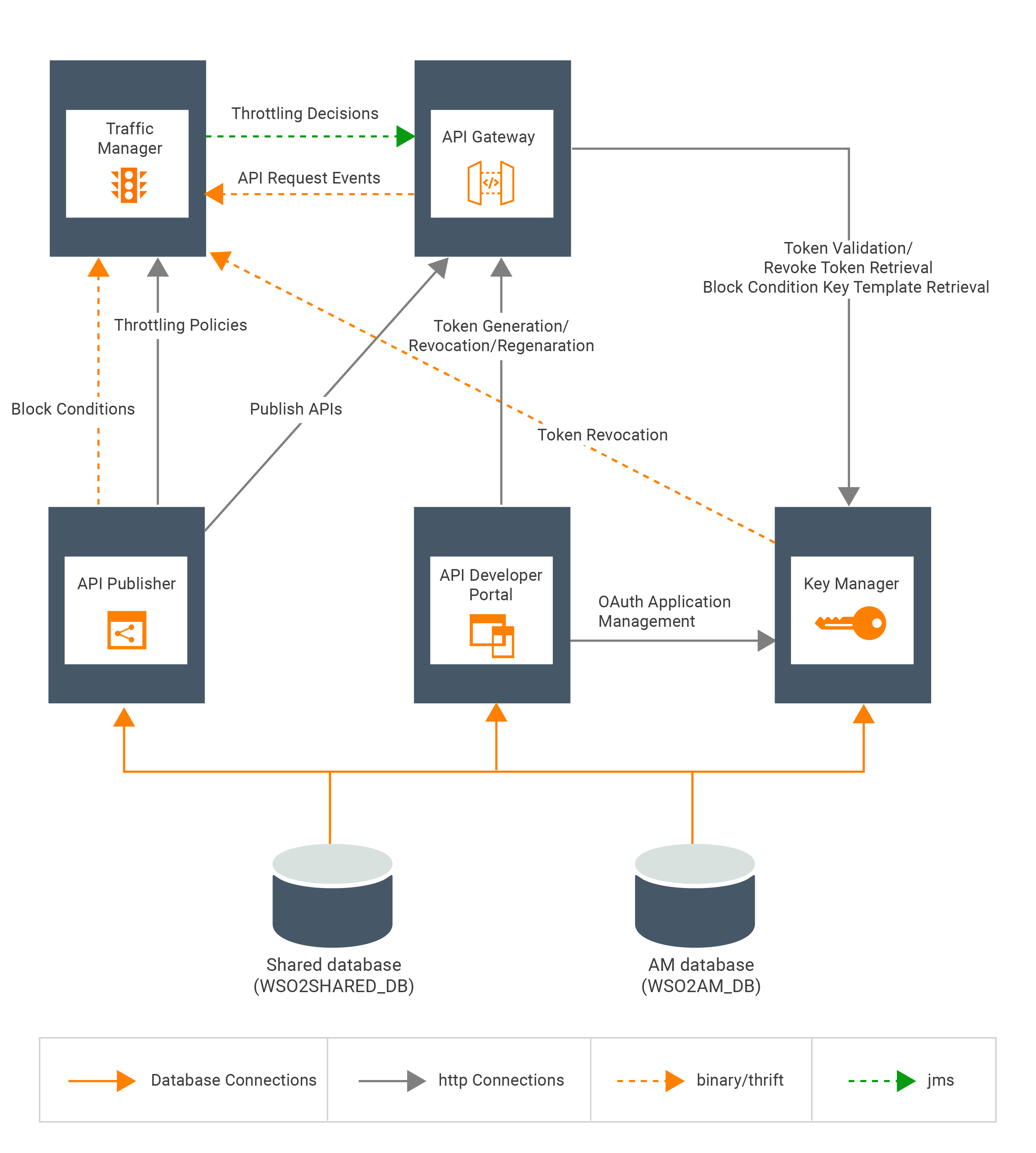
Understanding the WSO2 API-M architecture¶
WSO2 API Manager uses the following main components:
| Publisher | Enables API providers to easily publish their APIs, share documentation, provision API keys, and gather feedback on API features, quality, and usage. |
| Developer Portal | Enables consumers to self-register, discover API functionality, subscribe to APIs, evaluate them, and interact with API publishers. |
| Key Manager | Responsible for all security and key-related operations. |
| Gateway | Responsible for securing, protecting, managing, and scaling API calls. |
| Traffic Manager | Used to make a decision on throttling. |
For more information on the above, see the main components of a distributed system.
API Manager uses the following internal datastores to store temporary internal system data required by the local instance of the API Manager.
-
Carbon database - Stores general internal data related to the product.
-
Message Broker database - Stores the products message broker related data.
Note
Product users should not configure the above datastores to use an external RDBMS. These datastores will be managed locally by the respective product instance.
Additionally, API Manager uses the following databases, which are shared among the server nodes. These are responsible for storing user specific application data.
- API Manager database - Stores information related to the APIs along with the API subscription details. The Key Manager Server uses this database to store user access tokens that are used for verification of API calls. The API Manager database is also referred to as WSO2_AM_DB and apimgtdb.
- Shared database - Stores information related to users and API meta data. In previous versions of API Manager a distinction was made between the user management database(used to store users and user roles) and the registry database(used to store API meta data). But now the Shared database will unify these requirements under one single database instance. This helps to reduce the complexity of the deployment. The Shared database user related information is accessed by the Key Manager Server, Developer Portal, and Publisher. The Shared database API meta data is accessed by the Publisher and Developer Portal. Optionally if you are planning to create this setup for a multi-tenanted environment (create and work with tenants), the Gateway and Key Manager components will also need to access API meta data in this database. The Shared database is also referred to as WSO2_SHARED_DB and shareddb.
WSO2 API Manager components use the databases as follows:
API Manager
|
Shared Database
|
|
|---|---|---|
Publisher |
Used |
Used |
Developer Portal |
Used |
Used |
Key Manager |
Used |
Used |
Gateway |
Not used |
Used (in multi-tenancy mode/ in multiple gateway mode when Google Analytics is used) |
| Traffic Manager | Not used | Not used |
When we consider a distributed deployment of WSO2 API Manager, we have the option of separating the five components and clustering each component as needed. Let's look more closely at how the API Manager components are deployed separately.
Understanding the distributed deployment¶
In the following diagram, the five components are set up in a distributed deployment, and the five databases are connected to the relevant components respectively. The entire setup is also fronted by a load balancer.
Top