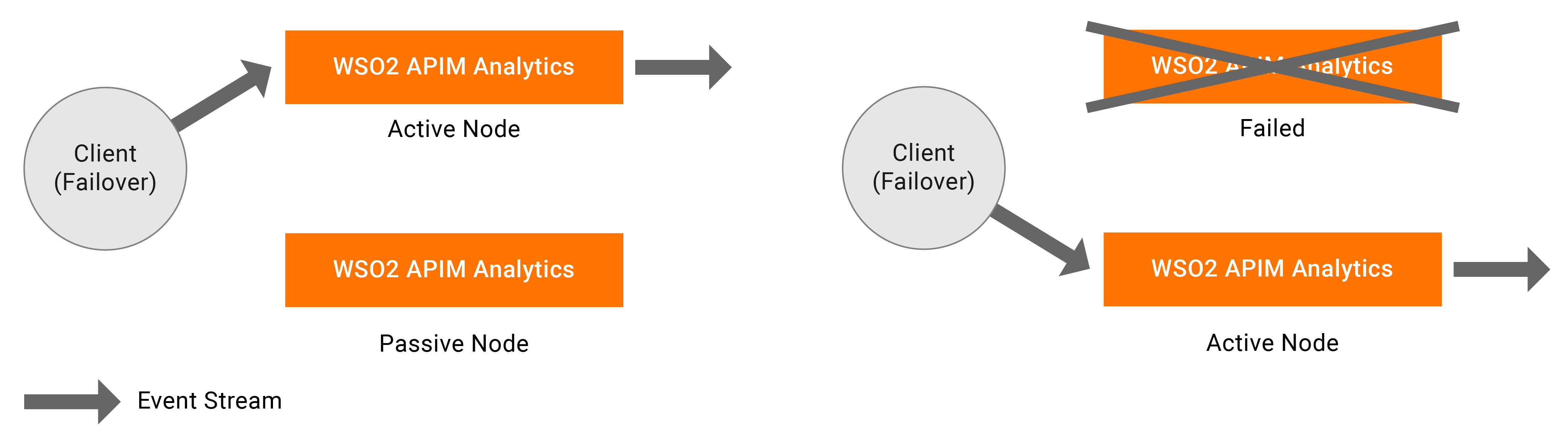
Configure Analytics Workers as Active-Passive¶
Minimum high availability (HA) deployment mainly focused on providing high availability which guarantees no data loss if the system suffer any failing due to several unforeseeable reasons. One of the main advantage of this is it uses minimum amount of infrastructure resources possible. Thus deployment pattern comprise of only two Streaming integration servers.
In minimum HA setup, one node is assigned as the active node while the other node is assigned as the passive node. Only the active node processes the incoming events and publishes the outgoing events. Internally, the active node publishes the events to the passive node, but the passive node does not process or send any events outside as mentioned earlier. In a scenario where the active node fails, the passive node is activated, and it starts receiving events and then publishes them from where the active node left off. Once the terminated (previously active) node restarts , it operates in the passive state. In the passive node, sources are in an inactive mode where they will not receive events into the system.
Note
The dashboard profile setup depends on the deployment. In an Active-Passive worker setup, you can have 2 JVMs for HA. As you have only 2 nodes, it is fine to use the dashboard of the same binary (pack).
Note
The ports that are open only in the active node at a given time include the Siddhi Store Query API endpoint to which
requests are sent by invoking the Siddhi Store REST API. These ports are configured in the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yaml file. For more information about this port configuration, see
Managing Stored Data via REST APIs.

When a failover occurs, the Siddhi Store Query API endpoint configured in node 2 (which becomes the currently active node) is opened, and all the Developer Portal query traffic is directed to that endpoint.
Note
In passive node databridge ports and Siddhi Store Query API endpoint are closed but the admin API are accessible.
For a two-node minimum HA cluster to work, only the active node should receive events. By design, you can only send events to active node. To achieve this, you can use a load balancing mechanism that sends events in failover manner. See the diagram below.
Prerequisites¶
In order to configure a minimum HA cluster, the following prerequisites must be completed:
- It is recommended to run this setup with two CPUs. Each CPU should have four cores, and 4GB memory.
- Two binary packs of WSO2 APIM ANALYTICS must be available.
- A working RDBMS instance to be used for clustering of the 2 nodes.
- Download the MySQL connector from here.
Extract and find the mysql-connector-java-5..-bin.jar. Place this JAR in the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/libdirectory of both nodes. - In order to retrieve the state of the Siddhi Applications deployed in the system in case of a scenario where both the nodes fail, state persistence must be enabled for both nodes by specifying the same datasource/file location. For detailed instructions, see Configuring Database and File System State Persistence for more information.
- A load balancer or some other client-side data publishing mechanism that works in a failover manner must be available to publish events to one of the available nodes (i.e., to the active node).
Configuring a minimum HA cluster¶
There are three main configurations which need to be configured in order to setup a minimum HA cluster which can be categorized as below,
- Cluster Configuration
- Persistent configuration
- HA configurationNote
- Note that the following configurations need to be done in the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yamlfile for both the WSO2 API Analaytics nodes in the cluster. - If you need to run both APIM Analytics instances in the same host, make sure that you do a port offset to change the default ports in one of the hosts. For more information about the default ports, see Configuring Default Ports.
See below the steps and configuration details need to carry out to configure the HA cluster.
-
For each node, enter a unique ID for the id property under the wso2.carbon section. (e.g., id: wso2-am_analytics). This is used to identify each node within a cluster.
-
To allow the two nodes to use same persistence storage, you need to configure RDBMS persistence configuration under the state.persistence. The following is a configuration for db-based persistence (Persistent configuration).
- state.persistence: enabled: true intervalInMin: 1 revisionsToKeep: 2 persistenceStore: io.siddhi.distribution.core.persistence.DBPersistenceStore config: datasource: PERSISTENCE_DB # A datasource with this name should be defined in wso2.datasources namespace table: PERSISTENCE_TABLEThe datasource named PERSISTENCE_DB in the above configuration can be defined in the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yamlfile under thewso2.datasourcessection. Following is a sample datasource configuration.- name: PERSISTENCE_DB description: The MySQL datasource used for persistence jndiConfig: name: jdbc/PERSISTENCE_DB definition: type: RDBMS configuration: jdbcUrl: 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/PERSISTENCE_DB?useSSL=false' username: root password: root driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver maxPoolSize: 50 idleTimeout: 60000 connectionTestQuery: SELECT 1 validationTimeout: 30000 isAutoCommit: false -
To allow the two nodes in the cluster to coordinate effectively, configure carbon coordination by updating the cluster.config section of the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yamlas follows (Cluster Configuration):- To enable the cluster mode, set the enabled property to true.
- In order to cluster the two nodes together, enter the same ID as the group ID for both nodes (e.g., groupId: group-1).
- Enter the ID of the class that defines the coordination strategy for the cluster as shown in the example below. e.g., coordinationStrategyClass: org.wso2.carbon.cluster.coordinator.rdbms.RDBMSCoordinationStrategy
-
In the strategyConfig section, enter information as follows:
- For clustering of the two nodes to take place
-
datasource - Enter the name of the configured datasource shared by the nodes in the cluster as shown in the example below. Data handled by the cluster are persisted here.
Following is a sample datasource configuration for a MySQL datasource that should appear under the dataSources section of the
wso2.datasourcessection in the<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yaml. For detailed instructions of how to configure a datasource, see Configuring Datasources.#Sample MySQL datasource - name: WSO2_CLUSTER_DB description: The MySQL datasource used for Cluster Coordination jndiConfig: name: jdbc/WSO2ClusterDB definition: type: RDBMS configuration: jdbcUrl: 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/WSO2_CLUSTER_DB?useSSL=false' username: root password: root driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver maxPoolSize: 50 idleTimeout: 60000 connectionTestQuery: SELECT 1 validationTimeout: 30000 isAutoCommit: false -
heartbeatInterval - Define the time interval (in milliseconds) at which heartbeat pulse should occur for each node. Recommended value for it is 5000 milliseconds
-
heartbeatMaxRetry - Defines the number of times to wait till active node to become live again before passive node becomes active. Recommended value is 5 times.
-
eventPollingInterval - Define the time interval (in milliseconds) at which each node should listen for changes that occur in the cluster. Recommended value for it is 5000 milliseconds
-
Sample cluster configuration can be as below :
- cluster.config: enabled: true groupId: group-1 coordinationStrategyClass: org.wso2.carbon.cluster.coordinator.rdbms.RDBMSCoordinationStrategy strategyConfig: datasource: WSO2_CLUSTER_DB heartbeatInterval: 5000 heartbeatMaxRetry: 5 eventPollingInterval: 5000
-
Next add the deployment.config section to the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yamlfile with following configurations (HA configuration)- To enable 2 node minimum HA, set the type property to "ha".
- passiveNodeDetailsWaitTimeOutMillis - Time in milliseconds to wait till passive node details gets available in database so that active node can retrieve them
- passiveNodeDetailsRetrySleepTimeMillis - This defines how much time to sleep before retying to retrieve details again
- eventByteBufferQueueCapacity - Size of the queue which used to keep events in passive node
- byteBufferExtractorThreadPoolSize - Number worker threads which reads events from the queue in passive node
-
To configure the TCP server via which event synchronization is carried out from active node to passive node, add a subsection named eventSyncServer and enter information as follows:
- host - Hostname of the server where the TCP server is spawn up
- port - Port of the TCP server
- advertisedHost - When the host can be different from actual server host
- advertisedPort - When the port can be different from the actual port of the server
-
bossThreads - Define a number of boss threads for the TCP server to handle the connections.
Default value is 10.
-
workerThreads - Define a number of worker threads for the TCP server to handle the connections.
Default value is 10.
-
To configure the TCP client via which requests are sent to the SI cluster, add a subsection named eventSyncClientPool and add information as follows
-
maxActive - Define the maximum number of active connections that must be allowed in the TCP client pool
Default value is 10.
-
maxTotal - Define the maximum number of total connections that must be allowed in the TCP client pool
Default value is 10.
-
maxIdle - Define the maximum number of idle connections that must be allowed in the TCP client pool
Default value is 10.
-
maxWait - Define the number of milliseconds the client pool must wait for an idle object when the connection pool.
Default value is 60000.
-
minEvictableIdleTimeInMillis - Define the minimum number of milliseconds an object can sit idle in the pool before it is eligible for eviction.
Default value is 120000
Note
Usage between host , port and advertisedHost and advertisedPort is , in a container environment actual server host and port can be different to exposing host and port. In such cases we can use advertisedHost and advertisedPort
Sample HA configuration can be as below :
- deployment.config: type: ha passiveNodeDetailsWaitTimeOutMillis: 300000 passiveNodeDetailsRetrySleepTimeMillis: 500 eventByteBufferQueueCapacity: 20000 byteBufferExtractorThreadPoolSize: 5 eventSyncServer: host: localhost port: 9893 advertisedHost: localhost advertisedPort: 9893 bossThreads: 10 workerThreads: 10 eventSyncClientPool: maxActive: 10 maxTotal: 10 maxIdle: 10 maxWait: 60000 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 120000 -
-
Configure APIM_ANALYTICS_DB in
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yaml
- name: APIM_ANALYTICS_DB
description: "The datasource used for APIM statistics aggregated data."
jndiConfig:
name: jdbc/APIM_ANALYTICS_DB
definition:
type: RDBMS
configuration:
jdbcUrl: "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/APIM_ANALYTICS_DB_1?useSSL=false"
password: pass
username: root
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
minIdle: 5
maxPoolSize: 50
idleTimeout: 60000
connectionTestQuery: SELECT 1
validationTimeout: 30000
isAutoCommit: false
- If you are configure analytics for WSO2 Micro Gateway, import the
appropriate DB script from
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/wso2/worker/dbscripts/apimgt/
Starting the cluster¶
-
Save the required Siddhi applications in the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/wso2/worker/deployment/siddhi-filesdirectory in both nodes. In order to ensure that the Siddhi applications are completely synchronized between the active and the passive node, they must be added to the siddhi-files directory before the server startup. However, the synchronization can take place effectively even if the Siddhi applications are added while the server is running. -
Start both servers by navigating to
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/binand issuing the following command:
If the cluster is correctly configured, the following CLI logs can be viewed without any error logs:For Windows: server.bat For Linux : ./server.shNote
In deploying Siddhi applications in a two node minimum HA cluster, it is recommended to use a content synchronization mechanism since Siddhi applications must be deployed to both server nodes. You can use a common shared file system such as Network File System (NFS) or any other shared file system that is available. You need to mount the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/wso2/worker/deployment/siddhi-filesdirectory of the two nodes to the shared file system.Note
To start two WSO2 SI Nodes in the same machine, the listenerConfigurations under the wso2.transport.http namespace in the
<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yamlfile must be updated to listen to different ports. The offset property under the ports section of the wso2.carbon section found in the<APIM_ANALYTICS_HOME>/conf/worker/deployment.yamlshould also be changed in one SI instance to avoid conflicts when starting both servers.